1.Identification
1.1GHS Product identifier
1.2Other means of identification
1.3Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use
1.4Supplier's details
1.5Emergency phone number
2.Hazard identification
2.1Classification of the substance or mixture
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 4
2.2GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
2.3Other hazards which do not result in classification
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients
3.1Substances
4.First-aid measures
4.1Description of necessary first-aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
In case of skin contact
Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
In case of eye contact
Rinse thoroughly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and consult a physician.
If swallowed
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
4.2Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
SYMPTOMS: Symptoms of exposure to this compound via ingestion include diabetes mellitus, hallucinations, distorted perceptions, cardiac effects, nausea, vomiting, changes in regional blood flow, dermatitis, anaphylaxis and decreased blood pressure. Other symptoms via ingestion include headache, dizziness, flushing, hypotension, tachycardia, fatigue and edema. It also causes dilation of coronary arteries and arterioles, reduced oxygen requirements, decreased platelet aggregation, weakness, heartburn, muscle cramps, tremor, nervousness, mood changes, palpitation, dyspnea, wheezing, cough, nasal congestion, sore throat, chest congestion, diarrhea, constipation flatulence, muscle inflammation, joint stiffness, shakiness, blurred vision, difficulties in balance, jitteriness, sleep disturbances, pruritus, urticaria, fever, sweating, chills, sexual difficulties and syncopal episodes. It can cause bradycardia, lethargy and anginal pain. It can also cause improved contractility and segmental ventricular function, increased heart rate and cardiac output, and increased peripheral blood flow due to arterial dilation (with no change in venous tone). It can cause negative inotropy, excessive vasodilation, depression of the sinus nodal rate, A-V nodal conduction disturbances, digital dysesthesia, sedation and aggravation of myocardial ischemia. Somnolence may occur. ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition this compound emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides.
4.3Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessary
Generally, overdosage with nifedipine leading to pronounced hypotension calls for active cardiovascular support including monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory function, elevation of extremities, judicious use of calcium infusion, pressor agents and fluids. Clearance of nifedipine would be expected to be prolonged in patients with impaired liver function. Since nifedipine is highly protein bound, dialysis is not likely to be of any benefit; however, plasmapheresis may be beneficial.
5.Fire-fighting measures
5.1Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Fires involving this material can be controlled with a dry chemical, carbon dioxide or Halon extinguisher. A water spray may also be used.
5.2Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Flash point data for this chemical are not available; however, it is probably combustible.
5.3Special protective actions for fire-fighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures
6.1Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2Environmental precautions
Prevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so. Do not let product enter drains. Discharge into the environment must be avoided.
6.3Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Pick up and arrange disposal. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed containers for disposal.
7.Handling and storage
7.1Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Nifedipine liquid-filled capsules should be protected from light and moisture and stored in tight, light-resistant containers at a temperature of 15-25°C, and extended-release tablets of the drug should be protected from light and moisture and stored in tight, light-resistant containers at a temperature less than 30°C.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection
8.1Control parameters
Occupational Exposure limit values
no data available
Biological limit values
no data available
8.2Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE)
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Wear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protection
Wear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazards
no data available
9.Physical and chemical properties
10.Stability and reactivity
10.1Reactivity
no data available
10.2Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
10.3Possibility of hazardous reactions
NIFEDIPINE is sensitive to light.
10.4Conditions to avoid
no data available
10.5Incompatible materials
no data available
10.6Hazardous decomposition products
When heated to decomposition, it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
11.Toxicological information
Acute toxicity
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
no data available
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
STOT-single exposure
no data available
STOT-repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
12.Ecological information
12.1Toxicity
12.2Persistence and degradability
no data available
12.3Bioaccumulative potential
An estimated BCF of 13 was calculated for Nifedipine(SRC), using a log Kow of 2.20(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4Mobility in soil
The Koc of Nifedipine is estimated as 370(SRC), using a log Kow of 2.20(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this estimated Koc value suggests that Nifedipine is expected to have moderate mobility in soil.
12.5Other adverse effects
no data available
13.Disposal considerations
13.1Disposal methods
Product
The material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packaging
Containers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information
14.1UN Number
14.2UN Proper Shipping Name
14.3Transport hazard class(es)
14.4Packing group, if applicable
14.5Environmental hazards
14.6Special precautions for user
no data available
14.7Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Code
no data available
 Deutsche
Deutsche Español
Español français
français italiano
italiano português
português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 العربية
العربية русский
русский bahasa Indonesia
bahasa Indonesia Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

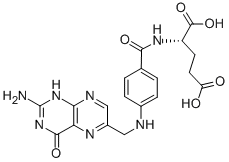 Folic acid,59-30-3
Folic acid,59-30-3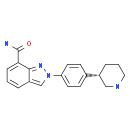 MK-4827 (HCl)
MK-4827 (HCl)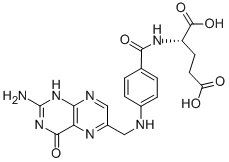 Folic acid
Folic acid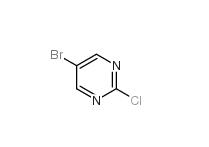 5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5
5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5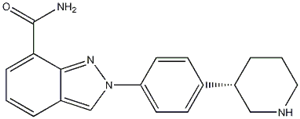 Niraparib
Niraparib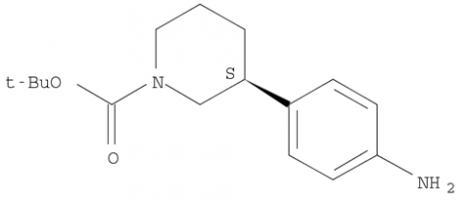 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate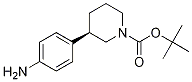 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate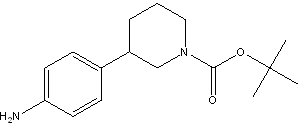 tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate![(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester](/data/attachment/201705/26/3446bd2b841689a5afc36447418dc476.png) (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester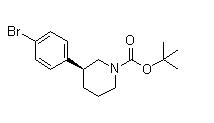 (3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester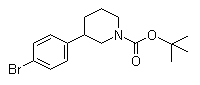 3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester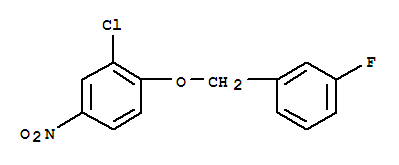 3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene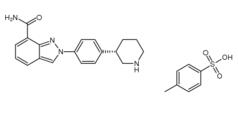 Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate
Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate![N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/da41ae70b523a458db70333bd1059362.png) N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide![2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/d3114dd994f3dda3142cba7d326bcede.jpg) 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide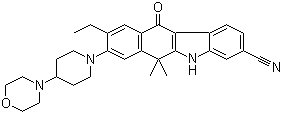 Alectinib
Alectinib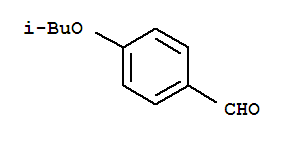 Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)
Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)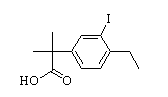 2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid
2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid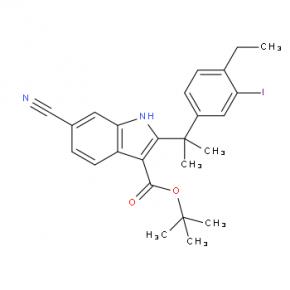 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate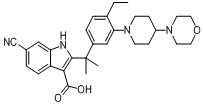 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid
6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid![9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/e48e5d316800efe6192ebfdeec6cf28c.gif) 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile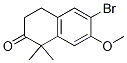 6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one
6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one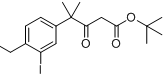 tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate
tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate![9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/fe98529212eb834b17a38f13138a35bf.png) 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile![9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride](/data/attachment/201705/28/36e5363f0c9f92378b75195743e2abb2.jpg) 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride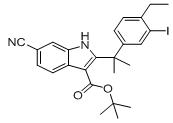 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate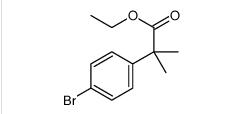 ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate
ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate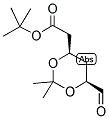 ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate
ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate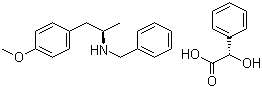 (2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
(2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine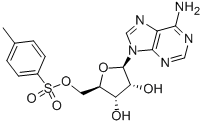 5-Tosyladenosine
5-Tosyladenosine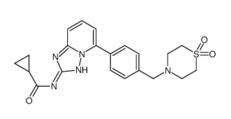 Filgotinib
Filgotinib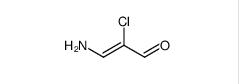 3-amino-2-chloroacrolein
3-amino-2-chloroacrolein![2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201706/03/2e19d959128718d26901f9909d7b9342.jpg) 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide![11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine](/data/attachment/201706/03/1549d9affee63ead337049001f25d9fa.jpg) 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine
11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine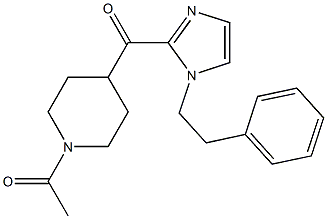 1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE
1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE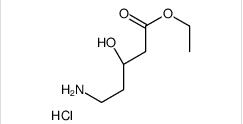 ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride
ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride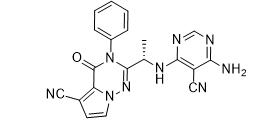 LAS191954 free base
LAS191954 free base![tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate](/data/attachment/201706/03/8a3c0fcdeb9ed744fc854cf248d4d53e.jpg) tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate
tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate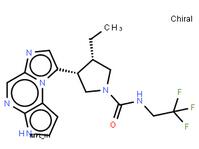 ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2
ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2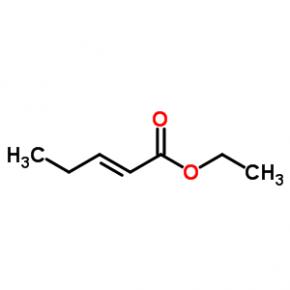 ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate
ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate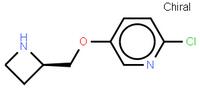 abt594 Intermediate
abt594 Intermediate LOXO101 Intermediate 2
LOXO101 Intermediate 2 LOXO101 Intermediate 1
LOXO101 Intermediate 1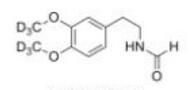 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2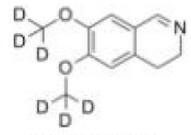 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1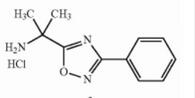 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate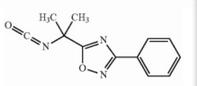 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2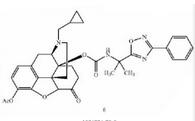 Naldemedine
Naldemedine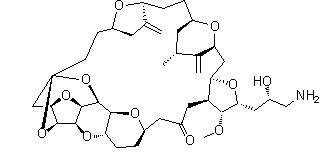 Eribulin
Eribulin![2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-, 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,](/data/attachment/201706/03/3575f40dcc389832ca73cc99972a645b.gif.thumb.jpg) 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,
2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,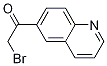 2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone
2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone![6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline](/data/attachment/201706/07/27ae4307b53f4294590fb8f914894490.jpg) 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline
6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline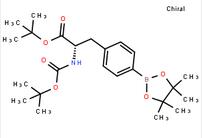 tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate
tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate![7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine](/data/attachment/201706/07/24ba6100528abe0753ad9e82ef8dc810.gif) 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine
7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine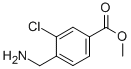 methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate
methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate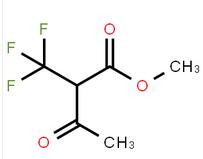 methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate
methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate![2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/07/22aadd4c55094254a681014935f56827.jpg) 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester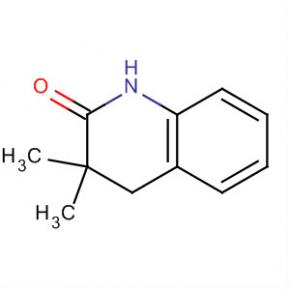 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl
2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl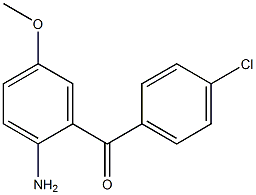 Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)
Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)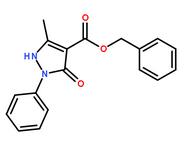 benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate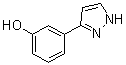 3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol
3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol 4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline
4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol![Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)](/data/attachment/201706/07/c4adcbada0ef372ae46cbaed643dd18e.jpg) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)
Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)![2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy](/data/attachment/201706/07/e0e9b5769a45af836d70be4140043125.gif.thumb.jpg) 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy
2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy![2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/07/5754ee36bdfbf4148f45632422f563b9.jpg) 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide![2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/47a8b3c98aef0b9ba378c4b7c6cef435.jpg) 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide![N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/beda6f8f4655aa74d3646cfc7621fb20.jpg) N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide
N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide (R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane
(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane![4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl] 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]](/data/attachment/201706/09/b600ffca12695094db2c5f6045cb6685.jpg) 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]
4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]![9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID](/data/attachment/201706/09/d6b395bbfb23e628be7d536d9cc2b512.gif) 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID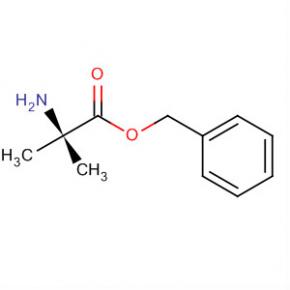 Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester
Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester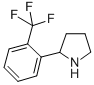 2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE
2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE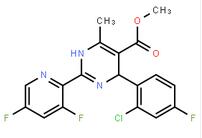 (-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
(-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester![2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/09/11c6e17ba89840528c5461ae5350df33.gif) 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl estermethanone [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone](/data/attachment/201706/09/ca947be16560699c92609cd96b352c02.png.thumb.jpg) [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone
[4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone![Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl](/data/attachment/201706/10/ce0d621896c03bdb67e3b184103e84ff.png.thumb.jpg) Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl
Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl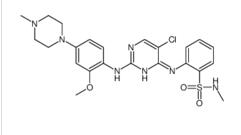 ALK inhibitor 2
ALK inhibitor 2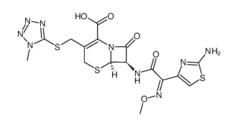 Cefmenoxime hydrochloride
Cefmenoxime hydrochloride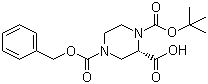 (S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid
(S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid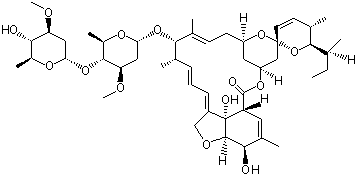 Avermectin
Avermectin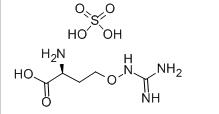 L-CANAVANINE SULFATE
L-CANAVANINE SULFATE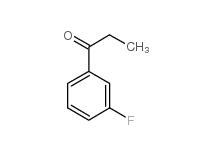 3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4
3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4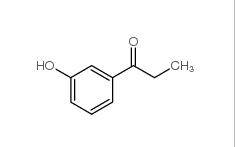 3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5
3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5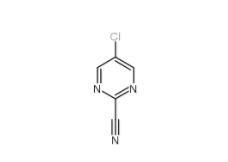 2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8
2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8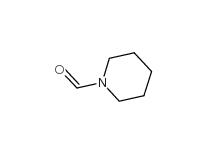 N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8
N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8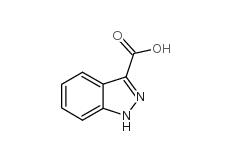 Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3
Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3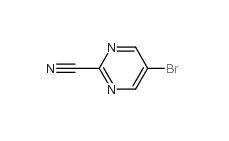 5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9
5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9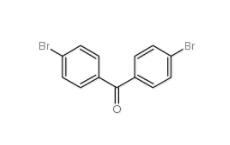 4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2
4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2![1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8](/data/attachment/201901/28/b183df1e648eca4396ad0d319a1254bc.jpg) 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8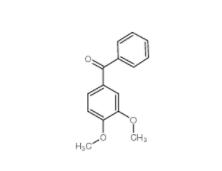 4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6
4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6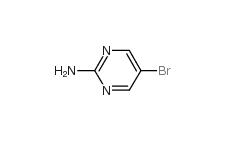 2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1
2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1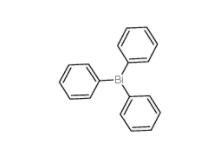 Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8
Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8![3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4](/data/attachment/201901/28/d6294d1dabcee85ee04792b0c0e255c0.jpg) 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4
3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4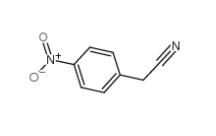 4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5
4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5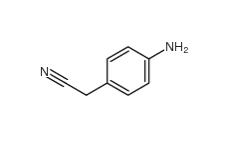 2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0
2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0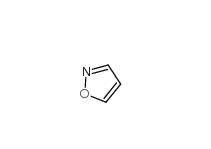 isoxazole 288-14-2
isoxazole 288-14-2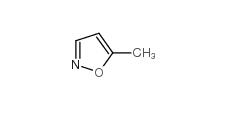 5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6
5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6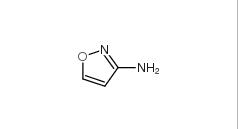 3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1
3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1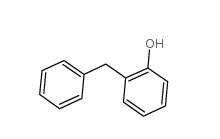 2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4
2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4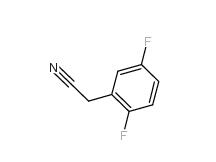 2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8
2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8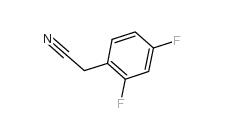 2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9
2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9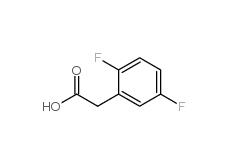 2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5
2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5 2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3
2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3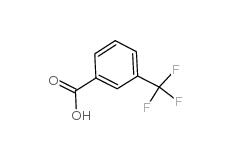 3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2
3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3](/data/attachment/201901/29/22b99245cb0bbcd2d86f238725d9fb9d.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9](/data/attachment/201901/29/7dbc74a276a4c124b9460222442fd80f.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9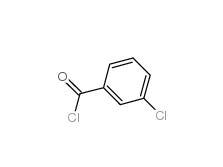 3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2
3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2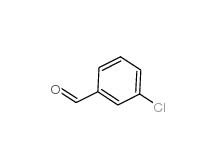 3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2
3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2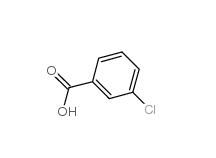 3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8
3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8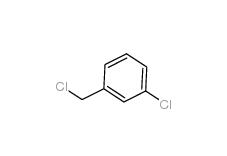 3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2
3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2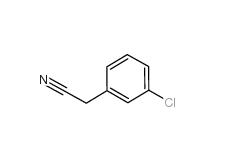 3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5
3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5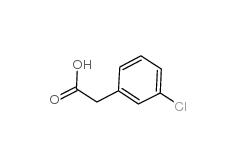 2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5
2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5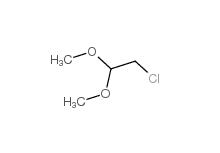 Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2
Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2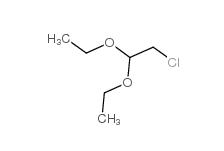 Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5
Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5 2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1
2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1 2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6
2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6 2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3
2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3 2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0
2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0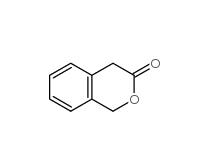 3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7
3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7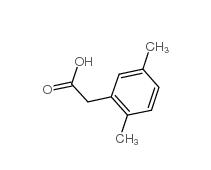 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5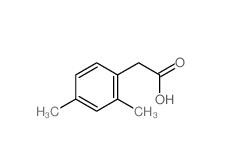 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0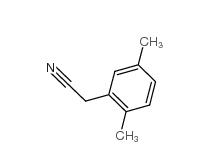 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7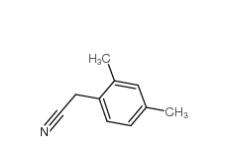 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8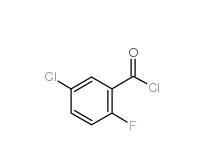 5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6
5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6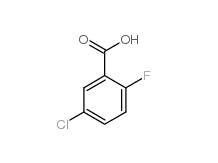 5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9
5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9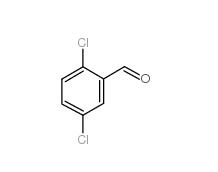 2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5
2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5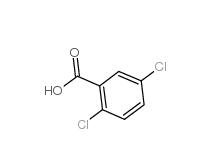 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3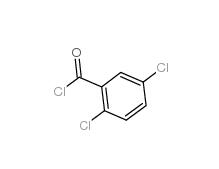 2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5
2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5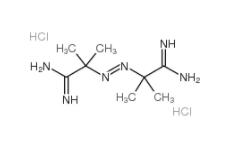 2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4
2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4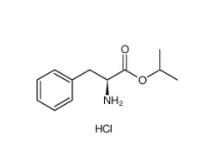 L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7
L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7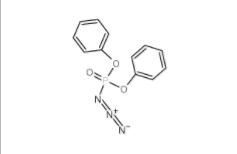 Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9
Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9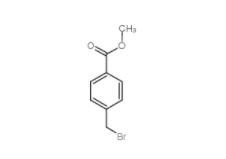 Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3
Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3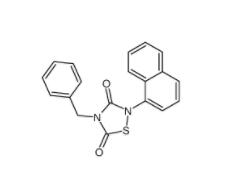 Tideglusib 865854-05-3
Tideglusib 865854-05-3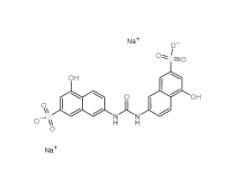 Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2
Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2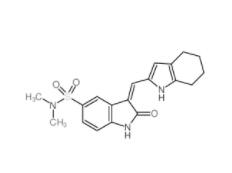 SU 6656 330161-87-0
SU 6656 330161-87-0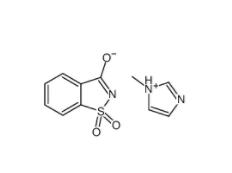 Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4
Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4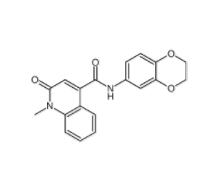 CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8
CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8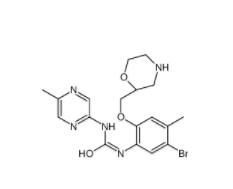 Rabusertib 911222-45-2
Rabusertib 911222-45-2 Salermide 1105698-15-4
Salermide 1105698-15-4 EST 88321-09-9
EST 88321-09-9 SC79 305834-79-1
SC79 305834-79-1 C646 328968-36-1
C646 328968-36-1 1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4
1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4 Dp44mT 152095-12-0
Dp44mT 152095-12-0 Deguelin 522-17-8
Deguelin 522-17-8 PD168393 194423-15-9
PD168393 194423-15-9 YO01027 209984-56-5
YO01027 209984-56-5 DC10539 1822358-25-7
DC10539 1822358-25-7 8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4
8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4 YU238259 1943733-16-1
YU238259 1943733-16-1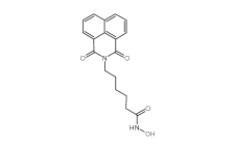 Scriptaid 287383-59-9
Scriptaid 287383-59-9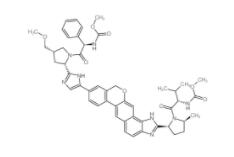 Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7
Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7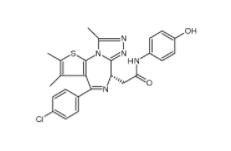 OTX015 202590-98-5
OTX015 202590-98-5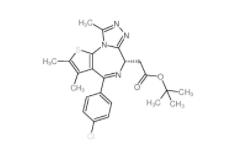 (+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4
(+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4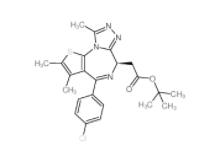 (-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5
(-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5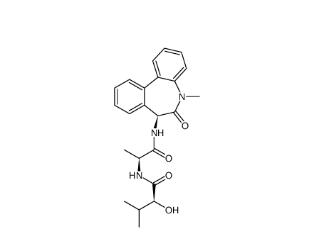 LY 900009 209984-68-9
LY 900009 209984-68-9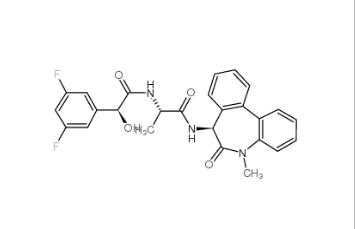 LY-411575 209984-57-6
LY-411575 209984-57-6![(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3 (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3](/data/attachment/201903/22/9e81dae7e0bdec56ac6052b1872d9626.jpg) (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3
(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3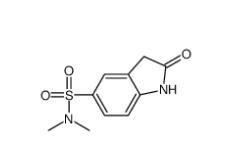 N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6
N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6![5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/50930df6d55412ac8f4da0724b497aaf.jpg) 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9
5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9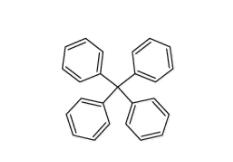 Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2
Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2![2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2](/data/attachment/201903/23/7e63bafe6c4b7e146e00c57dfca99672.jpg) 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2
2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2 1616380-54-1
1616380-54-1![N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9 N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/e26baac537719657acd9f1f55568401d.jpg) N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9
N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9![N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0 N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0](/data/attachment/201903/23/7d2bbd100c8322ae16168937617e1bb2.jpg) N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0
N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0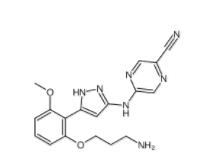 5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1
5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1![3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6](/data/attachment/201903/23/07bf6fd99e81033df0c83039ccdde036.jpg) 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6
3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6![3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3](/data/attachment/201903/23/f69ad7342d131146640e0c88f73e9a25.jpg) 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3
3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3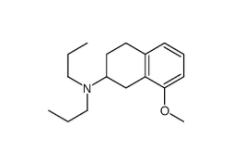 8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7
8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7![4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7](/data/attachment/201903/23/bb4110673d0676f81860d708092eb660.jpg) 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7
4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7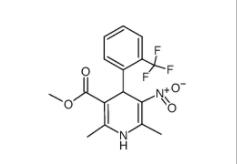 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4![2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4](/data/attachment/201903/23/b396a2326dddb511aae497b01fbd4c77.jpg) 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4
2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4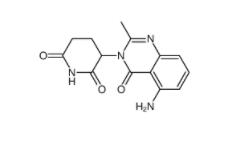 CC-122 1015474-32-4
CC-122 1015474-32-4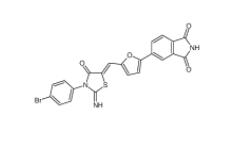 Bioymifi 1420071-30-2
Bioymifi 1420071-30-2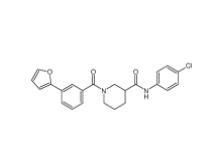 N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8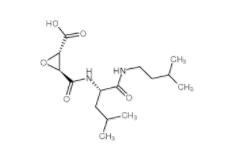 E-64C 76684-89-4
E-64C 76684-89-4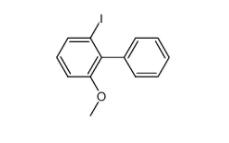 2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1
2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1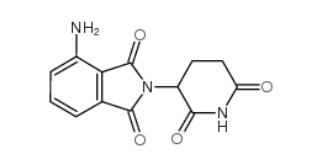 pomalidomide 19171-19-8
pomalidomide 19171-19-8 4EP-Directory listing
4EP-Directory listing Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9
Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9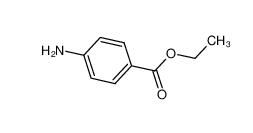 benzocaine 94-09-7
benzocaine 94-09-7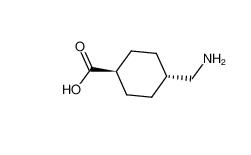 tranexamic acid 1197-18-8
tranexamic acid 1197-18-8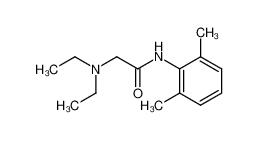 lidocaine 137-58-6
lidocaine 137-58-6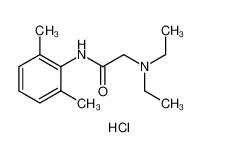 lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9
lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9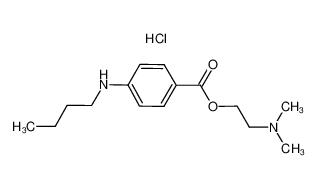 Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0
Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0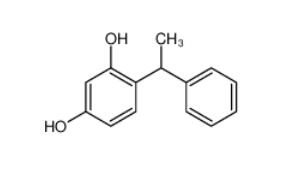 4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8
4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8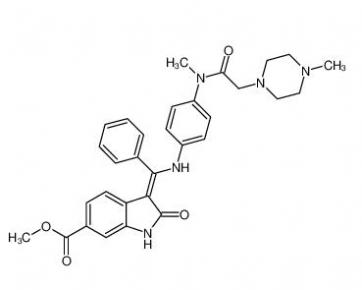 Nintedanib 656247-17-5
Nintedanib 656247-17-5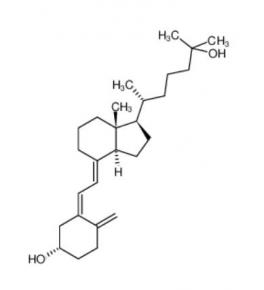 calcidiol 19356-17-3
calcidiol 19356-17-3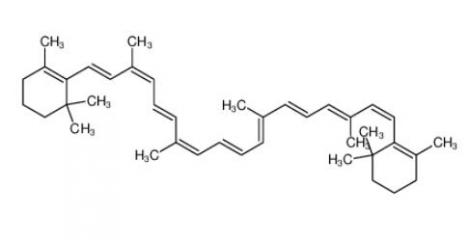 β-carotene 7235-40-7
β-carotene 7235-40-7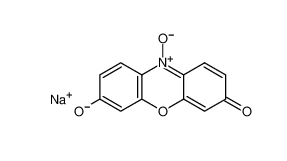 Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8
Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8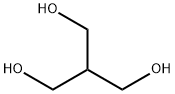 4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL
4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL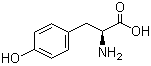 L-Tyrosine 60-18-4
L-Tyrosine 60-18-4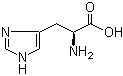 L-Histidine 71-00-1
L-Histidine 71-00-1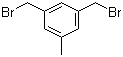 3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3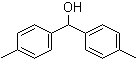 Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8
Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8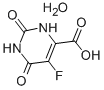 5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4
5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4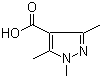 1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7
1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7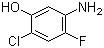 5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8
5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8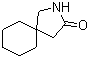 Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9
Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9 1EP-Directory listing
1EP-Directory listing![[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3 [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3](/data/attachment/202211/10/9756043560e11c17cf958f3ed54d541a.png.thumb.jpg) [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3
[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3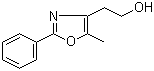 2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4
2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4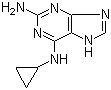 2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7
2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7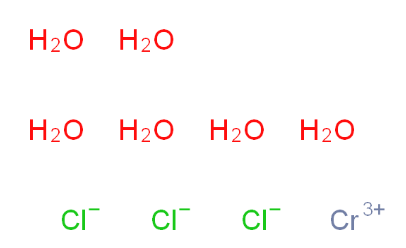 Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5
Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5 2EP-Directory listing 2
2EP-Directory listing 2 3EP-Directory listing 3
3EP-Directory listing 3




