1.Identification
1.1GHS Product identifier
| Product name | 2-butenoic acid |
|---|
1.2Other means of identification
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | But-2-enoic acid |
1.3Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Food additives -> Flavoring Agents |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
1.4Supplier's details
| Fax |
|---|
1.5Emergency phone number
| Emergency phone number | |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
2.Hazard identification
2.1Classification of the substance or mixture
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 4
Acute toxicity - Dermal, Category 4
Skin corrosion, Category 1C
Serious eye damage, Category 1
2.2GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
| Pictogram(s) | 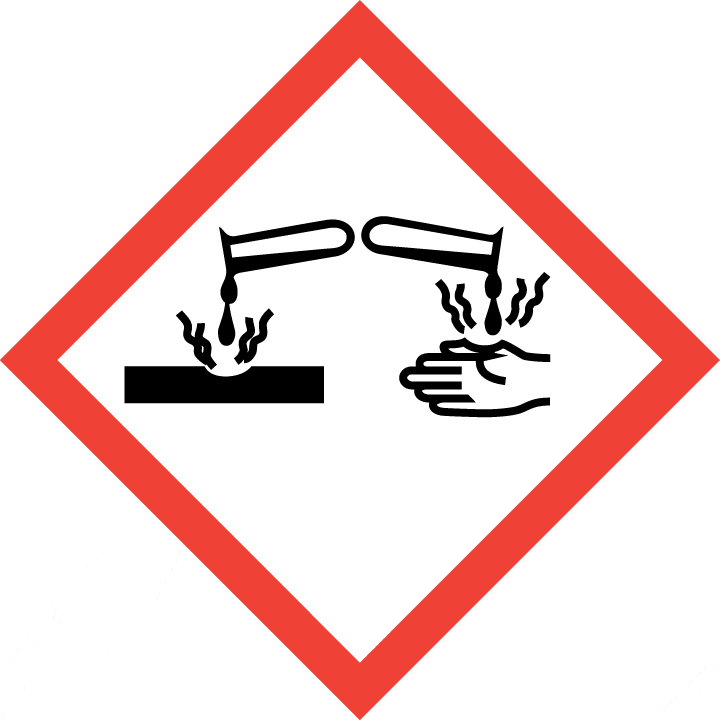  |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statement(s) | H302 Harmful if swallowed H312 Harmful in contact with skin H314 Causes severe skin burns and eye damage |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P260 Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. |
| Response | P301+P312 IF SWALLOWED: Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/u2026if you feel unwell. P330 Rinse mouth. P302+P352 IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water/... P312 Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/u2026if you feel unwell. P321 Specific treatment (see ... on this label). P362+P364 Take off contaminated clothing and wash it before reuse. P301+P330+P331 IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353 IF ON SKIN (or hair): Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with water [or shower]. P363 Wash contaminated clothing before reuse. P304+P340 IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. P310 Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/u2026 P305+P351+P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. |
| Storage | P405 Store locked up. |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
2.3Other hazards which do not result in classification
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients
3.1Substances
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-butenoic acid | 2-butenoic acid | 3724-65-0 | none | 100% |
4.First-aid measures
4.1Description of necessary first-aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
Fresh air, rest. Half-upright position. Artificial respiration may be needed. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contact
Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse skin with plenty of water or shower. Refer for medical attention .
In case of eye contact
First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowed
Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. Rest. Refer for medical attention .
4.2Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
Excerpt from ERG Guide 153 [Substances - Toxic and/or Corrosive (Combustible)]: TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. (ERG, 2016)
4.3Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessary
For immediate first aid - Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If victim is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask, device or pocket mask as trained. Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep victim quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Organic acids and related compounds/
5.Fire-fighting measures
5.1Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
If material on fire or involved in fire: Use water in flooding quantities as fog. Solid streams of water may be ineffective. Cool all affected containers with flooding quantities of water. Apply water from as far a distance as possible. Use "alcohol" foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
5.2Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Excerpt from ERG Guide 153 [Substances - Toxic and/or Corrosive (Combustible)]: Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Those substances designated with a (P) may polymerize explosively when heated or involved in a fire. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form. (ERG, 2016)
5.3Special protective actions for fire-fighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures
6.1Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2Environmental precautions
Consult an expert! Personal protection: complete protective clothing including self-contained breathing apparatus. Let solidify. Sweep spilled substance into covered containers. Then store and dispose of according to local regulations.
6.3Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Pick up and arrange disposal. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed containers for disposal.
7.Handling and storage
7.1Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Separated from food and feedstuffs, bases, oxidants and reducing agents. Dry. Keep in the dark.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection
8.1Control parameters
Occupational Exposure limit values
no data available
Biological limit values
no data available
8.2Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE)
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Wear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protection
Wear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazards
no data available
9.Physical and chemical properties
| Physical state | A white crystalline solid. Shipped as either a solid or liquid. |
|---|---|
| Colour | MONOCLINIC NEEDLES OR PRISMS (FROM WATER OR PETROLEUM ETHER) |
| Odour | no data available |
| Melting point/ freezing point | 73u00baC |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 181u00baC |
| Flammability | Combustible. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | no data available |
| Flash point | 88u00baC |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 745 DEG F (396 DEG C) |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | no data available |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | In water:soluble |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | Log Kow = 0.72 /isomer not specified/ |
| Vapour pressure | 0.19 mm Hg ( 20 u00b0C) |
| Density and/or relative density | 1.027 |
| Relative vapour density | 2.97 (vs air) |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
10.Stability and reactivity
10.1Reactivity
no data available
10.2Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
10.3Possibility of hazardous reactions
MODERATE, WHEN EXPOSED TO HEAT OR FLAMECROTONIC ACID is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in it to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
10.4Conditions to avoid
no data available
10.5Incompatible materials
no data available
10.6Hazardous decomposition products
Thermal decomposition products include carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. /Organic acids and related compounds/
11.Toxicological information
Acute toxicity
- Oral: no data available
- Inhalation: no data available
- Dermal: no data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
no data available
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
STOT-single exposure
no data available
STOT-repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
12.Ecological information
12.1Toxicity
- Toxicity to fish: no data available
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: no data available
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
12.2Persistence and degradability
Crotonic acid (mixture) was identified as being amenable to anaerobic biodegradation(1). Anaerobic bacteria isolated from mesophilic digester sludge acclimatized with 4-chlorobutyrate tentatively classified in the genus Clostridium, degraded crotonate to butyrate, acetate, and hydrogen(2). Ilyobacter polytropus anaerobically degraded crotonate to butyrate and acetate(2). Crotonate was degraded by an anaerobic bacterium to butyrate and acetate(3). After a lag period of 2 days, crotonic acid (isomer not specified) was metabolized, at a rate of 200 mg/l day, by anaerobic bacteria acclimated to acetate culture(4). Crotonic acid (isomer not specifed) reached 44% of its theoretical BOD in 5 days using a sewage inoculum(5).
12.3Bioaccumulative potential
An estimated BCF value of 2.1 was calculated for crotonic acid(SRC), using a measured log Kow of 0.72(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this BCF value suggests that bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4Mobility in soil
The Koc of crotonic acid is estimated as approximately 59(SRC), using a measured log Kow of 0.72(1) and a regression-derived equation(2,SRC). According to a classification scheme(3), this estimated Koc value suggests that crotonic acid is expected to have high mobility in soil(SRC).
12.5Other adverse effects
no data available
13.Disposal considerations
13.1Disposal methods
Product
The material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packaging
Containers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information
14.1UN Number
| ADR/RID: UN2823 | IMDG: UN2823 | IATA: UN2823 |
14.2UN Proper Shipping Name
| ADR/RID: CROTONIC ACID, SOLID |
| IMDG: CROTONIC ACID, SOLID |
| IATA: CROTONIC ACID, SOLID |
14.3Transport hazard class(es)
| ADR/RID: 8 | IMDG: 8 | IATA: 8 |
14.4Packing group, if applicable
| ADR/RID: III | IMDG: III | IATA: III |
14.5Environmental hazards
| ADR/RID: no | IMDG: no | IATA: no |
14.6Special precautions for user
no data available
14.7Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Code
no data available
15.Regulatory information
15.1Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-butenoic acid | 2-butenoic acid | 3724-65-0 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
 Deutsche
Deutsche Español
Español français
français italiano
italiano português
português 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 العربية
العربية русский
русский bahasa Indonesia
bahasa Indonesia Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt

 Folic acid,59-30-3
Folic acid,59-30-3 MK-4827 (HCl)
MK-4827 (HCl) Folic acid
Folic acid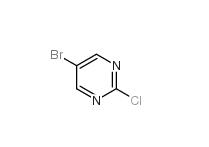 5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5
5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5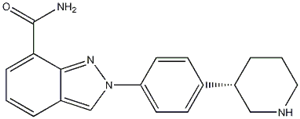 Niraparib
Niraparib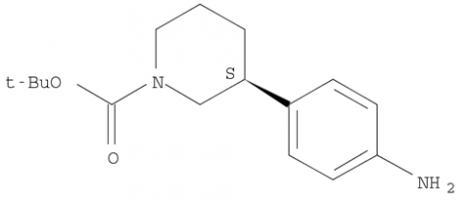 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate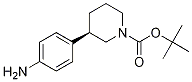 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate![(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester](/data/attachment/201705/26/3446bd2b841689a5afc36447418dc476.png) (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester 3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene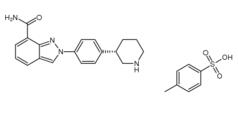 Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate
Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate![N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/da41ae70b523a458db70333bd1059362.png) N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide![2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/d3114dd994f3dda3142cba7d326bcede.jpg) 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide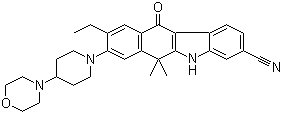 Alectinib
Alectinib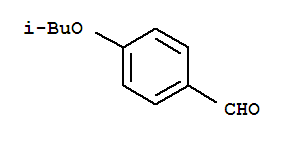 Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)
Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)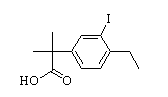 2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid
2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid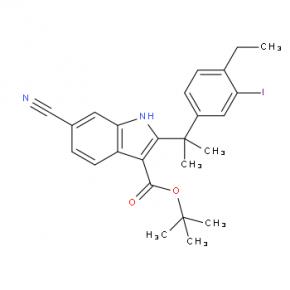 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate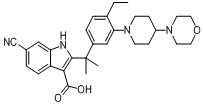 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid
6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid![9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/e48e5d316800efe6192ebfdeec6cf28c.gif) 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile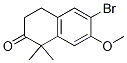 6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one
6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one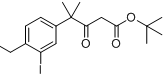 tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate
tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate![9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/fe98529212eb834b17a38f13138a35bf.png) 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile![9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride](/data/attachment/201705/28/36e5363f0c9f92378b75195743e2abb2.jpg) 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride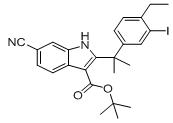 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate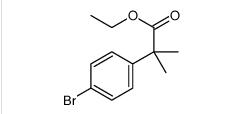 ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate
ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate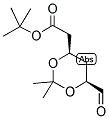 ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate
ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate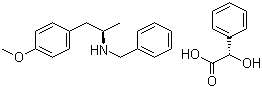 (2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
(2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine 5-Tosyladenosine
5-Tosyladenosine Filgotinib
Filgotinib 3-amino-2-chloroacrolein
3-amino-2-chloroacrolein![2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201706/03/2e19d959128718d26901f9909d7b9342.jpg) 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide![11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine](/data/attachment/201706/03/1549d9affee63ead337049001f25d9fa.jpg) 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine
11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine 1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE
1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE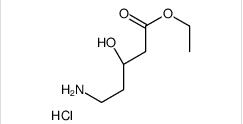 ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride
ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride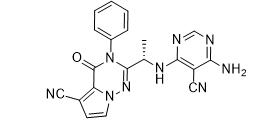 LAS191954 free base
LAS191954 free base![tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate](/data/attachment/201706/03/8a3c0fcdeb9ed744fc854cf248d4d53e.jpg) tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate
tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate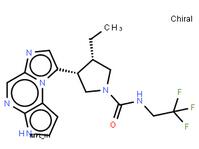 ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2
ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2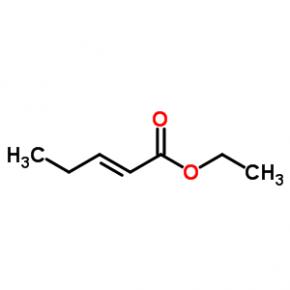 ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate
ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate abt594 Intermediate
abt594 Intermediate LOXO101 Intermediate 2
LOXO101 Intermediate 2 LOXO101 Intermediate 1
LOXO101 Intermediate 1 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2 Naldemedine
Naldemedine Eribulin
Eribulin![2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-, 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,](/data/attachment/201706/03/3575f40dcc389832ca73cc99972a645b.gif.thumb.jpg) 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,
2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-, 2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone
2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone![6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline](/data/attachment/201706/07/27ae4307b53f4294590fb8f914894490.jpg) 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline
6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate
tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate![7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine](/data/attachment/201706/07/24ba6100528abe0753ad9e82ef8dc810.gif) 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine
7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate
methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate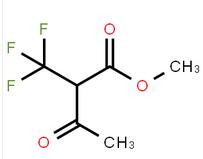 methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate
methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate![2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/07/22aadd4c55094254a681014935f56827.jpg) 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester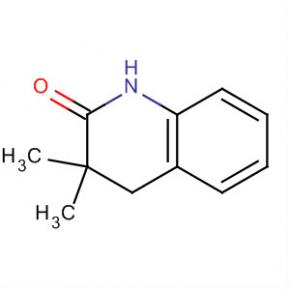 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl
2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl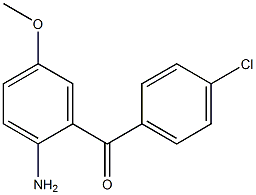 Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)
Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)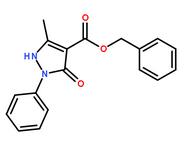 benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate 3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol
3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol 4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline
4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol![Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)](/data/attachment/201706/07/c4adcbada0ef372ae46cbaed643dd18e.jpg) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)
Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)![2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy](/data/attachment/201706/07/e0e9b5769a45af836d70be4140043125.gif.thumb.jpg) 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy
2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy![2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/07/5754ee36bdfbf4148f45632422f563b9.jpg) 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide![2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/47a8b3c98aef0b9ba378c4b7c6cef435.jpg) 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide![N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/beda6f8f4655aa74d3646cfc7621fb20.jpg) N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide
N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide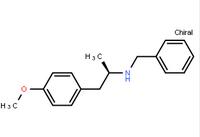 (R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane
(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane![4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl] 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]](/data/attachment/201706/09/b600ffca12695094db2c5f6045cb6685.jpg) 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]
4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]![9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID](/data/attachment/201706/09/d6b395bbfb23e628be7d536d9cc2b512.gif) 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID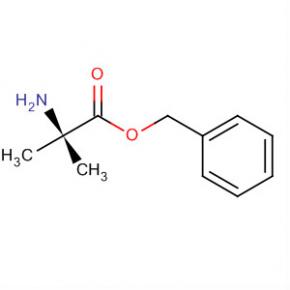 Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester
Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester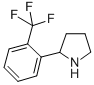 2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE
2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE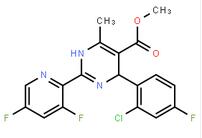 (-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
(-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester![2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/09/11c6e17ba89840528c5461ae5350df33.gif) 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl estermethanone [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone](/data/attachment/201706/09/ca947be16560699c92609cd96b352c02.png.thumb.jpg) [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone
[4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone![Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl](/data/attachment/201706/10/ce0d621896c03bdb67e3b184103e84ff.png.thumb.jpg) Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl
Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl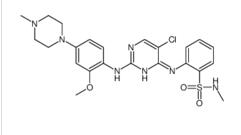 ALK inhibitor 2
ALK inhibitor 2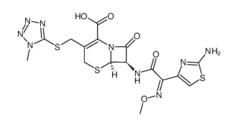 Cefmenoxime hydrochloride
Cefmenoxime hydrochloride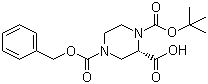 (S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid
(S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid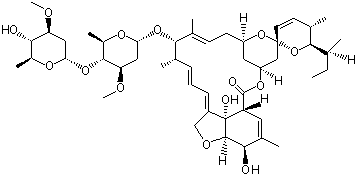 Avermectin
Avermectin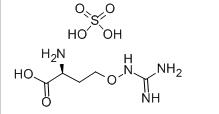 L-CANAVANINE SULFATE
L-CANAVANINE SULFATE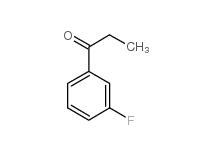 3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4
3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4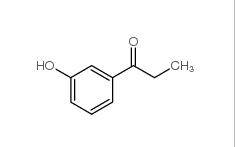 3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5
3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5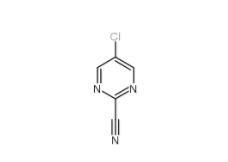 2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8
2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8 N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8
N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8 Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3
Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3 5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9
5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9 4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2
4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2![1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8](/data/attachment/201901/28/b183df1e648eca4396ad0d319a1254bc.jpg) 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8 4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6
4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6 2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1
2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1 Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8
Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8![3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4](/data/attachment/201901/28/d6294d1dabcee85ee04792b0c0e255c0.jpg) 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4
3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4 4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5
4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5 2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0
2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0 isoxazole 288-14-2
isoxazole 288-14-2 5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6
5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6 3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1
3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1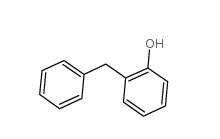 2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4
2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4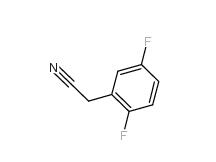 2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8
2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8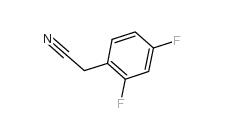 2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9
2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9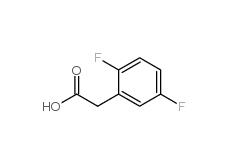 2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5
2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5 2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3
2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3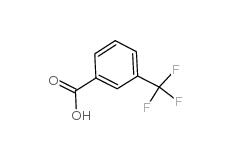 3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2
3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3](/data/attachment/201901/29/22b99245cb0bbcd2d86f238725d9fb9d.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9](/data/attachment/201901/29/7dbc74a276a4c124b9460222442fd80f.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9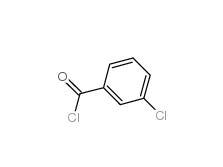 3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2
3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2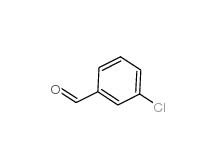 3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2
3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2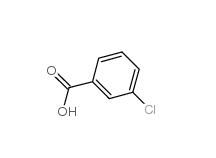 3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8
3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8 3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2
3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2 3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5
3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5 2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5
2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5 Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2
Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2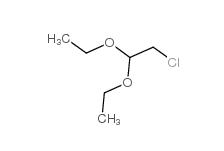 Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5
Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5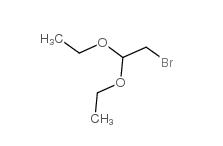 2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1
2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1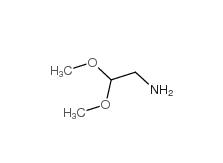 2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6
2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6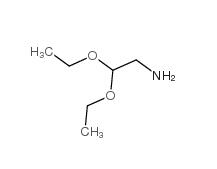 2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3
2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3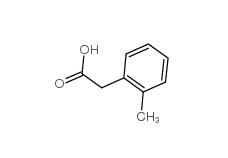 2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0
2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0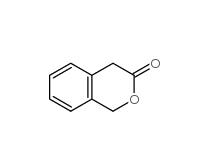 3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7
3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7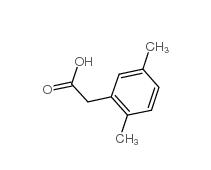 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5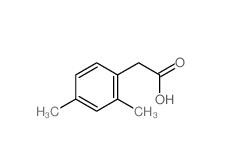 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0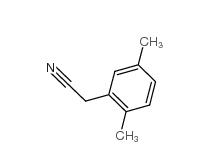 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7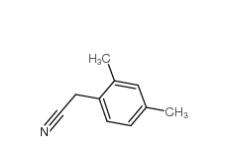 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8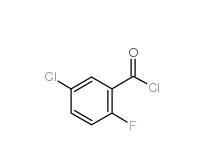 5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6
5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6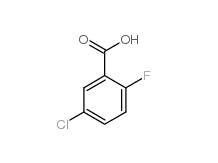 5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9
5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9 2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5
2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3 2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5
2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5 2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4
2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4 L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7
L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7 Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9
Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9 Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3
Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3 Tideglusib 865854-05-3
Tideglusib 865854-05-3 Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2
Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2 SU 6656 330161-87-0
SU 6656 330161-87-0 Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4
Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4 CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8
CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8 Rabusertib 911222-45-2
Rabusertib 911222-45-2 Salermide 1105698-15-4
Salermide 1105698-15-4 EST 88321-09-9
EST 88321-09-9 SC79 305834-79-1
SC79 305834-79-1 C646 328968-36-1
C646 328968-36-1 1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4
1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4 Dp44mT 152095-12-0
Dp44mT 152095-12-0 Deguelin 522-17-8
Deguelin 522-17-8 PD168393 194423-15-9
PD168393 194423-15-9 YO01027 209984-56-5
YO01027 209984-56-5 DC10539 1822358-25-7
DC10539 1822358-25-7 8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4
8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4 YU238259 1943733-16-1
YU238259 1943733-16-1 Scriptaid 287383-59-9
Scriptaid 287383-59-9 Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7
Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7 OTX015 202590-98-5
OTX015 202590-98-5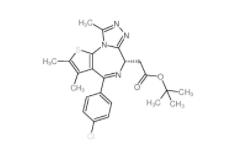 (+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4
(+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4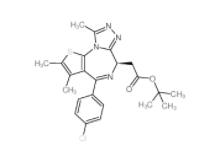 (-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5
(-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5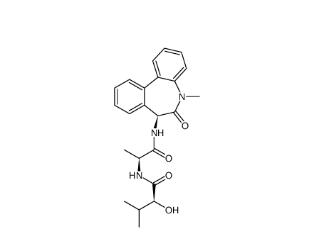 LY 900009 209984-68-9
LY 900009 209984-68-9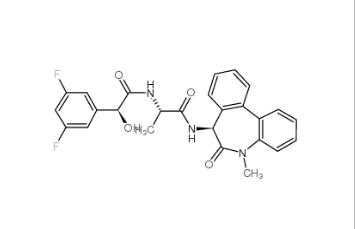 LY-411575 209984-57-6
LY-411575 209984-57-6![(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3 (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3](/data/attachment/201903/22/9e81dae7e0bdec56ac6052b1872d9626.jpg) (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3
(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3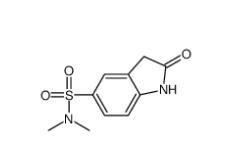 N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6
N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6![5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/50930df6d55412ac8f4da0724b497aaf.jpg) 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9
5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9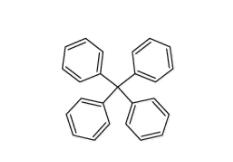 Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2
Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2![2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2](/data/attachment/201903/23/7e63bafe6c4b7e146e00c57dfca99672.jpg) 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2
2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2 1616380-54-1
1616380-54-1![N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9 N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/e26baac537719657acd9f1f55568401d.jpg) N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9
N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9![N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0 N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0](/data/attachment/201903/23/7d2bbd100c8322ae16168937617e1bb2.jpg) N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0
N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0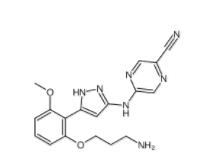 5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1
5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1![3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6](/data/attachment/201903/23/07bf6fd99e81033df0c83039ccdde036.jpg) 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6
3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6![3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3](/data/attachment/201903/23/f69ad7342d131146640e0c88f73e9a25.jpg) 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3
3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3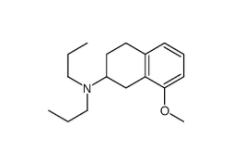 8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7
8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7![4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7](/data/attachment/201903/23/bb4110673d0676f81860d708092eb660.jpg) 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7
4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7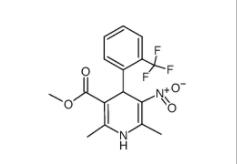 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4![2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4](/data/attachment/201903/23/b396a2326dddb511aae497b01fbd4c77.jpg) 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4
2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4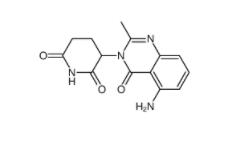 CC-122 1015474-32-4
CC-122 1015474-32-4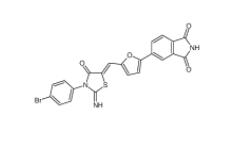 Bioymifi 1420071-30-2
Bioymifi 1420071-30-2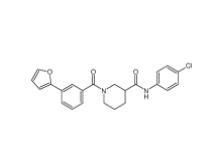 N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8 E-64C 76684-89-4
E-64C 76684-89-4 2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1
2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1 pomalidomide 19171-19-8
pomalidomide 19171-19-8 4EP-Directory listing
4EP-Directory listing Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9
Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9 benzocaine 94-09-7
benzocaine 94-09-7 tranexamic acid 1197-18-8
tranexamic acid 1197-18-8 lidocaine 137-58-6
lidocaine 137-58-6 lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9
lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9 Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0
Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0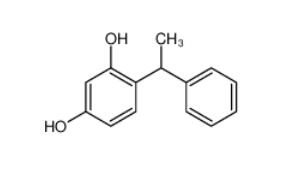 4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8
4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8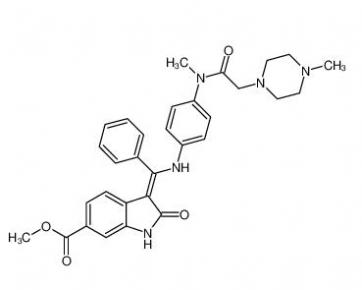 Nintedanib 656247-17-5
Nintedanib 656247-17-5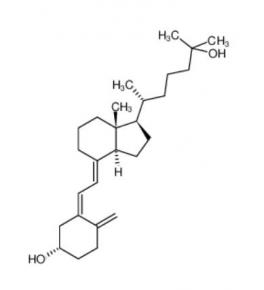 calcidiol 19356-17-3
calcidiol 19356-17-3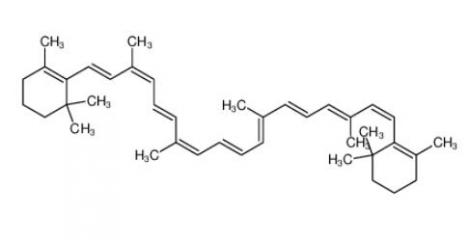 β-carotene 7235-40-7
β-carotene 7235-40-7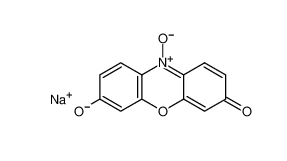 Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8
Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8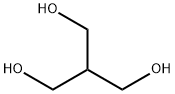 4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL
4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL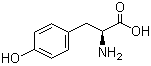 L-Tyrosine 60-18-4
L-Tyrosine 60-18-4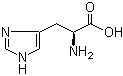 L-Histidine 71-00-1
L-Histidine 71-00-1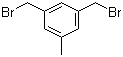 3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3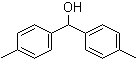 Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8
Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8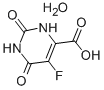 5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4
5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4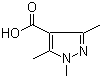 1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7
1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7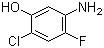 5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8
5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8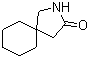 Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9
Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9 1EP-Directory listing
1EP-Directory listing![[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3 [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3](/data/attachment/202211/10/9756043560e11c17cf958f3ed54d541a.png.thumb.jpg) [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3
[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3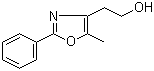 2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4
2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4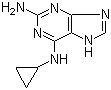 2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7
2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7 Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5
Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5 2EP-Directory listing 2
2EP-Directory listing 2 3EP-Directory listing 3
3EP-Directory listing 3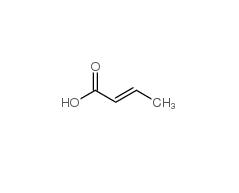

 C
C 
