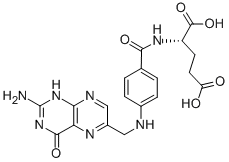
 Folic acid,59-30-3
Folic acid,59-30-3
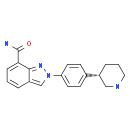 MK-4827 (HCl)
MK-4827 (HCl)
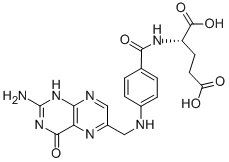 Folic acid
Folic acid
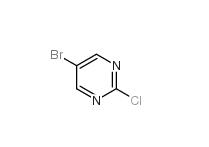 5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5
5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5
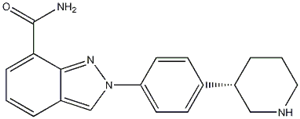 Niraparib
Niraparib
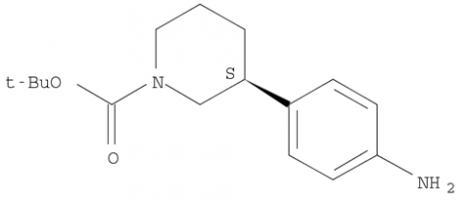 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
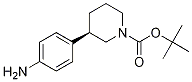 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
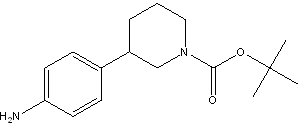 tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
![(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester](/data/attachment/201705/26/3446bd2b841689a5afc36447418dc476.png) (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
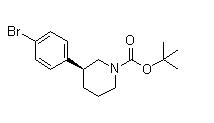 (3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
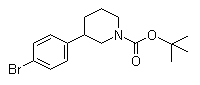 3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
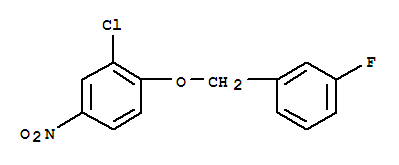 3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
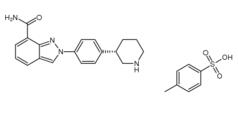 Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate
Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate
![N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/da41ae70b523a458db70333bd1059362.png) N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
![2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/d3114dd994f3dda3142cba7d326bcede.jpg) 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
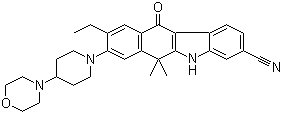 Alectinib
Alectinib
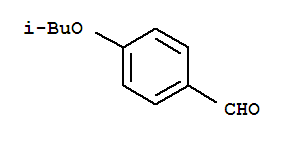 Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)
Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)
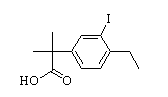 2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid
2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid
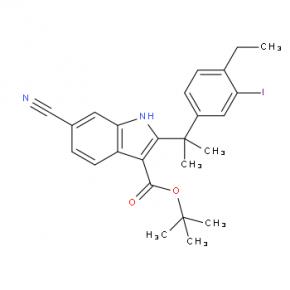 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
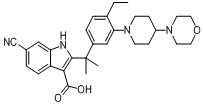 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid
6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid
![9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/e48e5d316800efe6192ebfdeec6cf28c.gif) 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
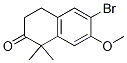 6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one
6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one
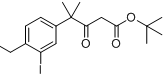 tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate
tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate
![9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/fe98529212eb834b17a38f13138a35bf.png) 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
![9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride](/data/attachment/201705/28/36e5363f0c9f92378b75195743e2abb2.jpg) 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
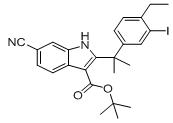 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
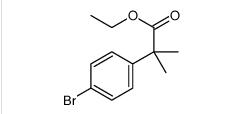 ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate
ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate
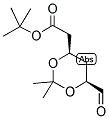 ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate
ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate
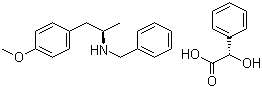 (2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
(2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
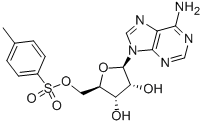 5-Tosyladenosine
5-Tosyladenosine
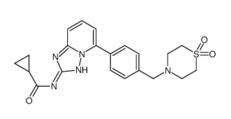 Filgotinib
Filgotinib
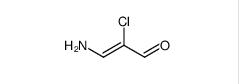 3-amino-2-chloroacrolein
3-amino-2-chloroacrolein
![2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201706/03/2e19d959128718d26901f9909d7b9342.jpg) 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
![11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine](/data/attachment/201706/03/1549d9affee63ead337049001f25d9fa.jpg) 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine
11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine
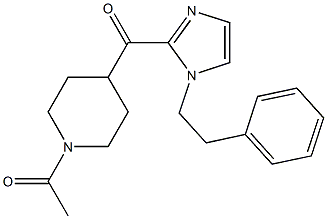 1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE
1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE
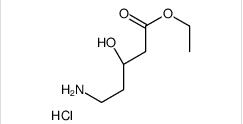 ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride
ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride
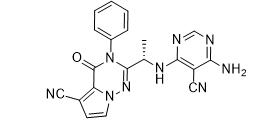 LAS191954 free base
LAS191954 free base
![tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate](/data/attachment/201706/03/8a3c0fcdeb9ed744fc854cf248d4d53e.jpg) tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate
tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate
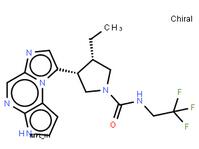 ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2
ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2
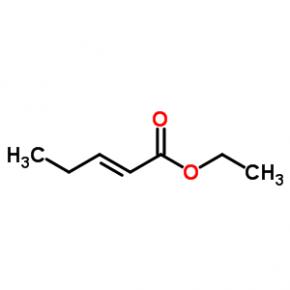 ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate
ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate
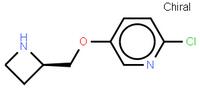 abt594 Intermediate
abt594 Intermediate
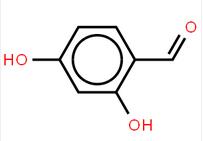 LOXO101 Intermediate 2
LOXO101 Intermediate 2
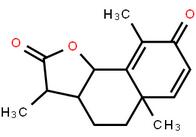 LOXO101 Intermediate 1
LOXO101 Intermediate 1
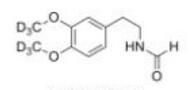 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2
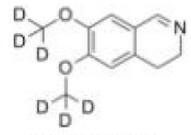 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1
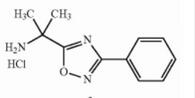 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate
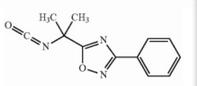 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2
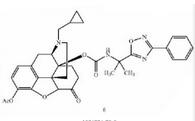 Naldemedine
Naldemedine
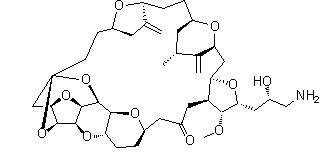 Eribulin
Eribulin
![2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-, 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,](/data/attachment/201706/03/3575f40dcc389832ca73cc99972a645b.gif.thumb.jpg) 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,
2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,
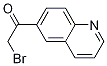 2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone
2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone
![6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline](/data/attachment/201706/07/27ae4307b53f4294590fb8f914894490.jpg) 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline
6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline
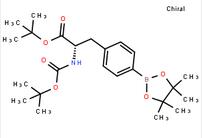 tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate
tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate
![7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine](/data/attachment/201706/07/24ba6100528abe0753ad9e82ef8dc810.gif) 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine
7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine
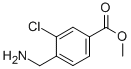 methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate
methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate
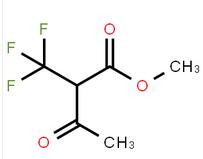 methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate
methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate
![2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/07/22aadd4c55094254a681014935f56827.jpg) 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
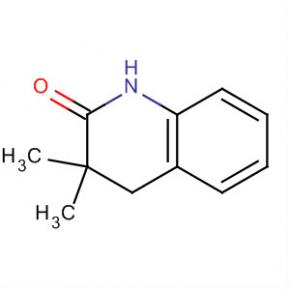 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl
2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl
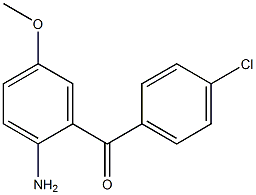 Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)
Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)
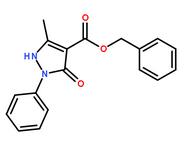 benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
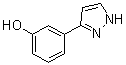 3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol
3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol
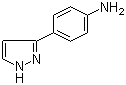 4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline
4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline
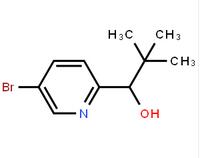 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol
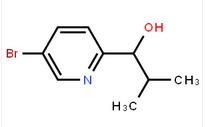 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol
![Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)](/data/attachment/201706/07/c4adcbada0ef372ae46cbaed643dd18e.jpg) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)
Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)
![2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy](/data/attachment/201706/07/e0e9b5769a45af836d70be4140043125.gif.thumb.jpg) 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy
2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy
![2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/07/5754ee36bdfbf4148f45632422f563b9.jpg) 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide
![2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/47a8b3c98aef0b9ba378c4b7c6cef435.jpg) 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide
![N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/beda6f8f4655aa74d3646cfc7621fb20.jpg) N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide
N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide
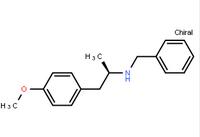 (R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane
(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane
![4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl] 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]](/data/attachment/201706/09/b600ffca12695094db2c5f6045cb6685.jpg) 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]
4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]
![9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID](/data/attachment/201706/09/d6b395bbfb23e628be7d536d9cc2b512.gif) 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
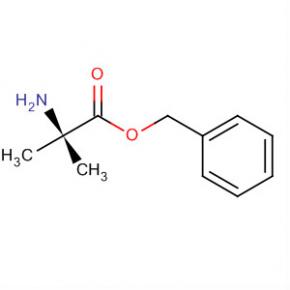 Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester
Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester
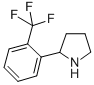 2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE
2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE
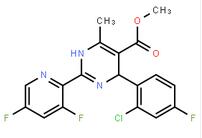 (-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
(-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
![2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/09/11c6e17ba89840528c5461ae5350df33.gif) 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
methanone [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone](/data/attachment/201706/09/ca947be16560699c92609cd96b352c02.png.thumb.jpg) [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone
[4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone
![Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl](/data/attachment/201706/10/ce0d621896c03bdb67e3b184103e84ff.png.thumb.jpg) Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl
Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl
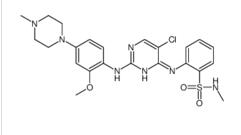 ALK inhibitor 2
ALK inhibitor 2
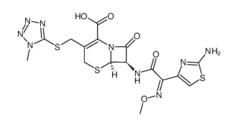 Cefmenoxime hydrochloride
Cefmenoxime hydrochloride
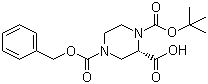 (S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid
(S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid
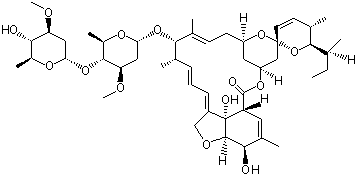 Avermectin
Avermectin
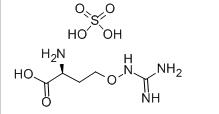 L-CANAVANINE SULFATE
L-CANAVANINE SULFATE
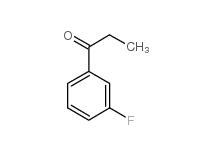 3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4
3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4
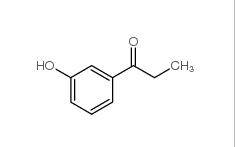 3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5
3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5
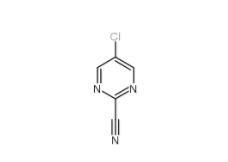 2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8
2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8
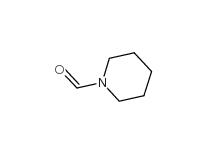 N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8
N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8
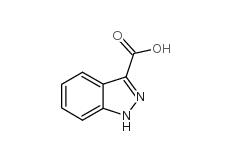 Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3
Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3
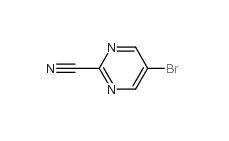 5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9
5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9
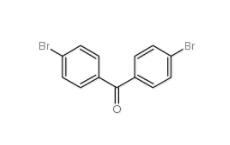 4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2
4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2
![1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8](/data/attachment/201901/28/b183df1e648eca4396ad0d319a1254bc.jpg) 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8
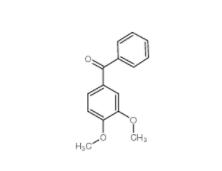 4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6
4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6
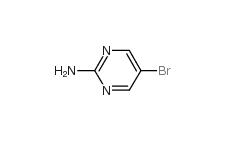 2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1
2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1
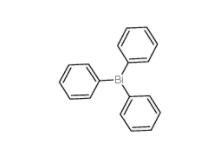 Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8
Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8
![3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4](/data/attachment/201901/28/d6294d1dabcee85ee04792b0c0e255c0.jpg) 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4
3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4
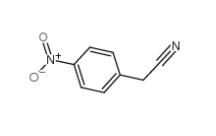 4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5
4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5
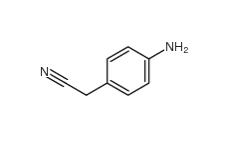 2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0
2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0
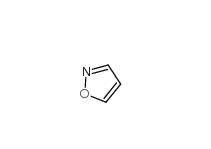 isoxazole 288-14-2
isoxazole 288-14-2
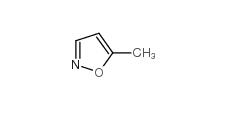 5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6
5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6
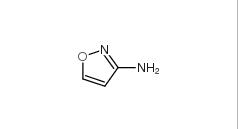 3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1
3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1
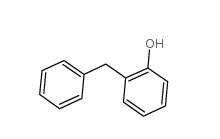 2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4
2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4
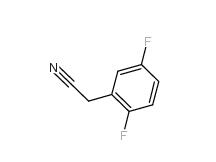 2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8
2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8
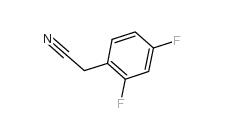 2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9
2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9
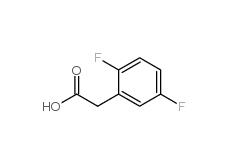 2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5
2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5
 2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3
2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3
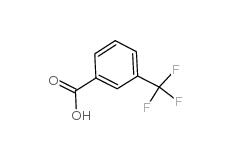 3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2
3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2
![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3](/data/attachment/201901/29/22b99245cb0bbcd2d86f238725d9fb9d.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3
![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9](/data/attachment/201901/29/7dbc74a276a4c124b9460222442fd80f.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9
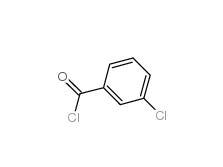 3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2
3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2
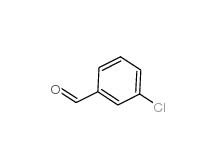 3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2
3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2
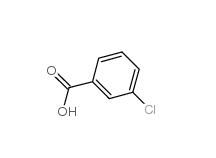 3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8
3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8
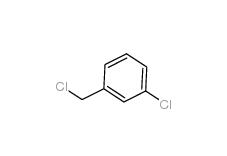 3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2
3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2
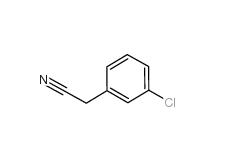 3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5
3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5
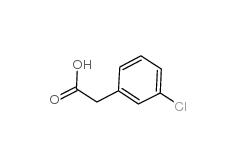 2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5
2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5
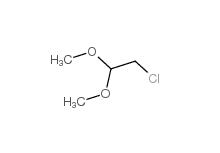 Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2
Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2
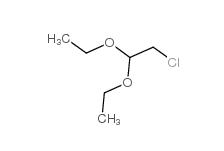 Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5
Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5
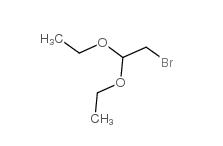 2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1
2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1
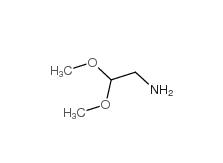 2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6
2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6
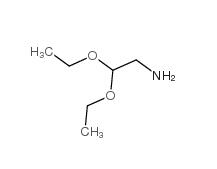 2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3
2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3
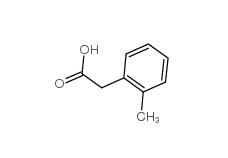 2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0
2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0
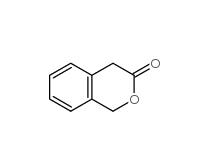 3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7
3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7
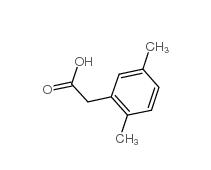 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5
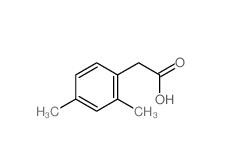 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0
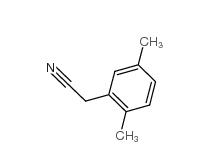 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7
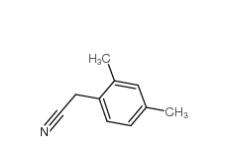 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8
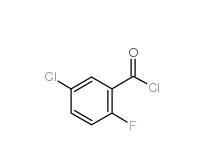 5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6
5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6
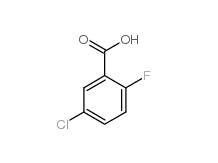 5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9
5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9
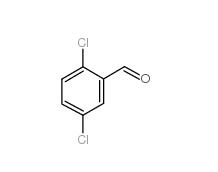 2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5
2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5
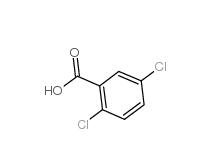 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3
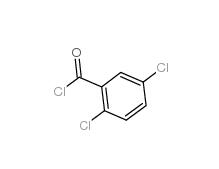 2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5
2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5
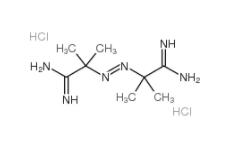 2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4
2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4
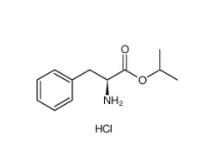 L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7
L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7
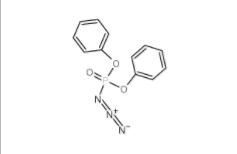 Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9
Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9
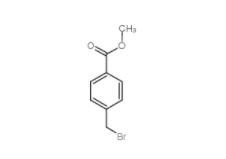 Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3
Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3
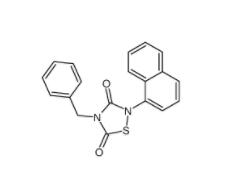 Tideglusib 865854-05-3
Tideglusib 865854-05-3
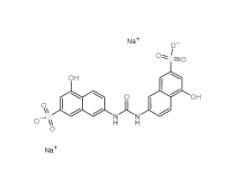 Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2
Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2
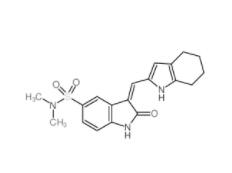 SU 6656 330161-87-0
SU 6656 330161-87-0
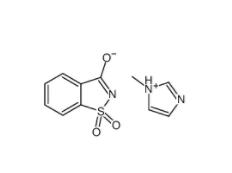 Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4
Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4
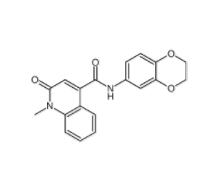 CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8
CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8
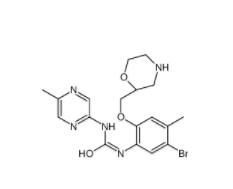 Rabusertib 911222-45-2
Rabusertib 911222-45-2
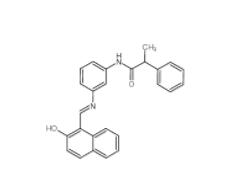 Salermide 1105698-15-4
Salermide 1105698-15-4
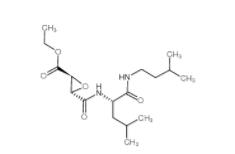 EST 88321-09-9
EST 88321-09-9
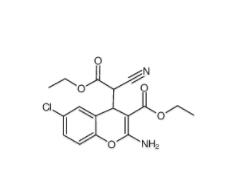 SC79 305834-79-1
SC79 305834-79-1
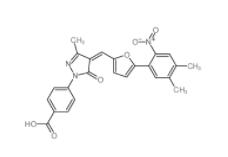 C646 328968-36-1
C646 328968-36-1
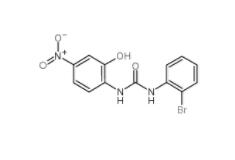 1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4
1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4
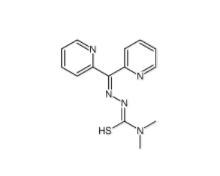 Dp44mT 152095-12-0
Dp44mT 152095-12-0
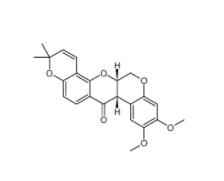 Deguelin 522-17-8
Deguelin 522-17-8
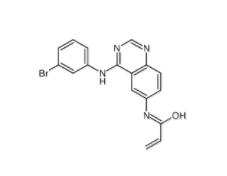 PD168393 194423-15-9
PD168393 194423-15-9
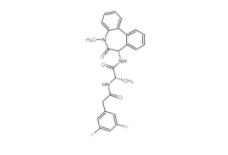 YO01027 209984-56-5
YO01027 209984-56-5
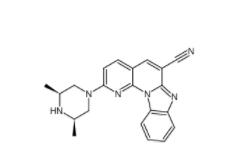 DC10539 1822358-25-7
DC10539 1822358-25-7
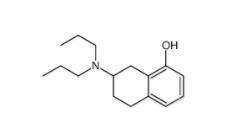 8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4
8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4
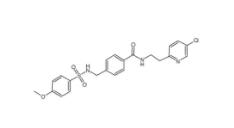 YU238259 1943733-16-1
YU238259 1943733-16-1
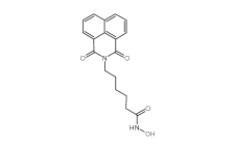 Scriptaid 287383-59-9
Scriptaid 287383-59-9
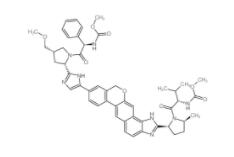 Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7
Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7
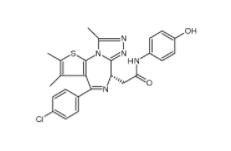 OTX015 202590-98-5
OTX015 202590-98-5
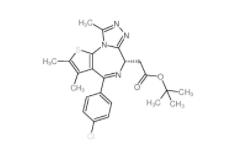 (+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4
(+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4
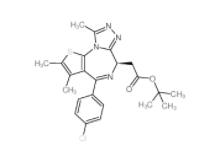 (-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5
(-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5
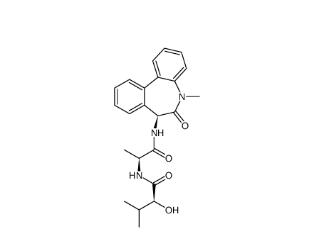 LY 900009 209984-68-9
LY 900009 209984-68-9
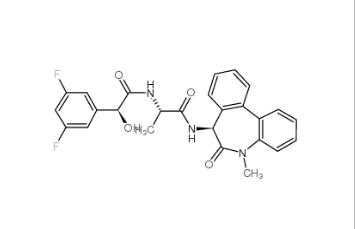 LY-411575 209984-57-6
LY-411575 209984-57-6
![(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3 (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3](/data/attachment/201903/22/9e81dae7e0bdec56ac6052b1872d9626.jpg) (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3
(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3
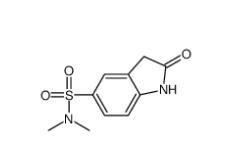 N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6
N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6
![5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/50930df6d55412ac8f4da0724b497aaf.jpg) 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9
5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9
 Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2
Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2
![2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2](/data/attachment/201903/23/7e63bafe6c4b7e146e00c57dfca99672.jpg) 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2
2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2
 1616380-54-1
1616380-54-1
![N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9 N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/e26baac537719657acd9f1f55568401d.jpg) N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9
N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9
![N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0 N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0](/data/attachment/201903/23/7d2bbd100c8322ae16168937617e1bb2.jpg) N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0
N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0
 5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1
5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1
![3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6](/data/attachment/201903/23/07bf6fd99e81033df0c83039ccdde036.jpg) 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6
3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6
![3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3](/data/attachment/201903/23/f69ad7342d131146640e0c88f73e9a25.jpg) 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3
3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3
 8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7
8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7
![4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7](/data/attachment/201903/23/bb4110673d0676f81860d708092eb660.jpg) 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7
4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7
 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4
![2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4](/data/attachment/201903/23/b396a2326dddb511aae497b01fbd4c77.jpg) 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4
2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4
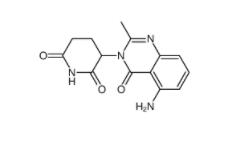 CC-122 1015474-32-4
CC-122 1015474-32-4
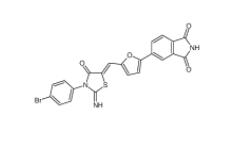 Bioymifi 1420071-30-2
Bioymifi 1420071-30-2
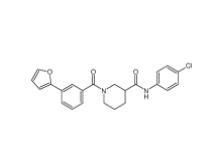 N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8
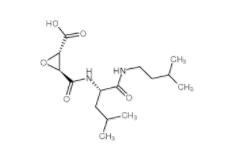 E-64C 76684-89-4
E-64C 76684-89-4
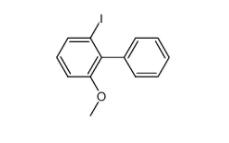 2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1
2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1
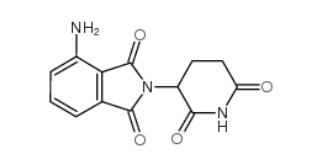 pomalidomide 19171-19-8
pomalidomide 19171-19-8
 4EP-Directory listing
4EP-Directory listing
 Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9
Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9
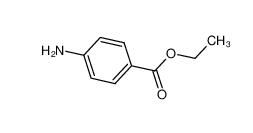 benzocaine 94-09-7
benzocaine 94-09-7
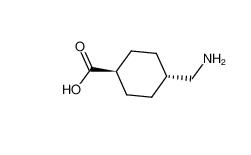 tranexamic acid 1197-18-8
tranexamic acid 1197-18-8
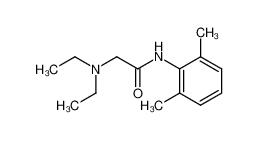 lidocaine 137-58-6
lidocaine 137-58-6
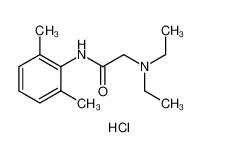 lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9
lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9
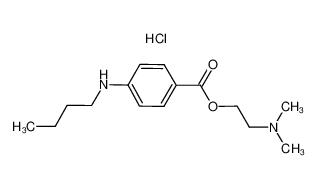 Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0
Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0
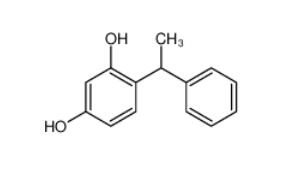 4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8
4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8
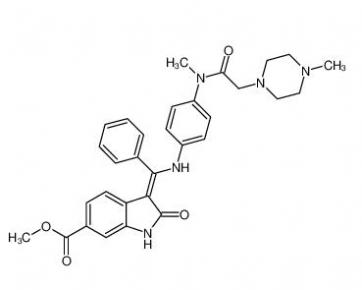 Nintedanib 656247-17-5
Nintedanib 656247-17-5
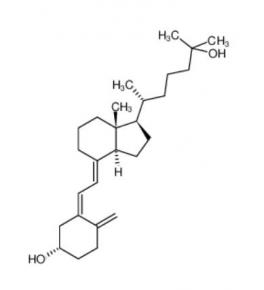 calcidiol 19356-17-3
calcidiol 19356-17-3
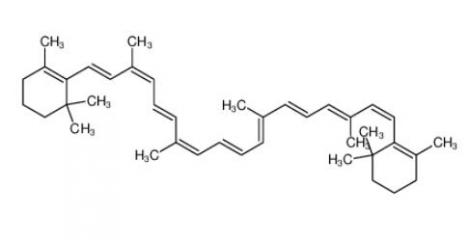 β-carotene 7235-40-7
β-carotene 7235-40-7
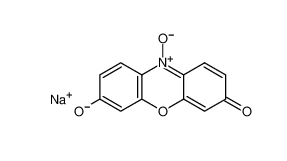 Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8
Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8
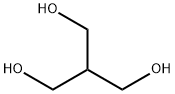 4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL
4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL
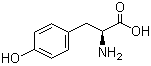 L-Tyrosine 60-18-4
L-Tyrosine 60-18-4
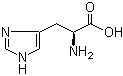 L-Histidine 71-00-1
L-Histidine 71-00-1
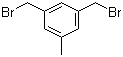 3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3
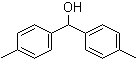 Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8
Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8
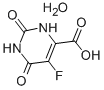 5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4
5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4
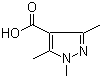 1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7
1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7
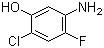 5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8
5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8
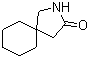 Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9
Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9
 1EP-Directory listing
1EP-Directory listing
![[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3 [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3](/data/attachment/202211/10/9756043560e11c17cf958f3ed54d541a.png.thumb.jpg) [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3
[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3
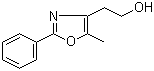 2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4
2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4
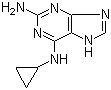 2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7
2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7
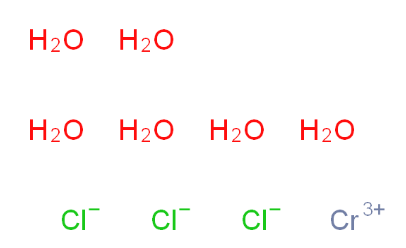 Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5
Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5
 2EP-Directory listing 2
2EP-Directory listing 2
 3EP-Directory listing 3
3EP-Directory listing 3