Product Name: Triamcinolone
Synonyms: 9α-Fluoro-16α-hydroxyprednisolone;9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17,21-tetrahydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione;TRIAMCINOLONE,USP;11b,16a,17a,21-Tetrahydroxy-9a-fluoro-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione;11b,16a,17a,21-Tetrahydroxy-9a-fluoro-D1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione;31: PN: US20030109453 SEQID: 30 claimed sequence;9a-Fluoro-11b,16a,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione;9a-Fluoro-11b,16a,17a,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
CAS: 124-94-7
MF: C21H27FO6
MW: 394.43
EINECS: 204-718-7
Product Categories: Biochemistry;Hydroxyketosteroids;Intermediates & Fine Chemicals;Pharmaceuticals;Steroid and Hormone;ARISTOCORT;Steroids;API
Mol File: 124-94-7.mol
Triamcinolone Structure
Triamcinolone Chemical Properties
Melting point 262-263 °C(lit.)
alpha 69 º (c=2, DMF)
Boiling point 587.5±50.0 °C(Predicted)
density 1.1703 (estimate)
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility DMF: soluble20 mg/mL
pka 11.57±0.70(Predicted)
form neat
color Crystals
optical activity [α]25/D +69°, c = 2 in DMF
Water Solubility 79.99mg/L(25 ºC)
Merck 9595
InChIKey GFNANZIMVAIWHM-OBYCQNJPSA-N
CAS DataBase Reference 124-94-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
NIST Chemistry Reference Triamcinolone(124-94-7)
EPA Substance Registry System Triamcinolone (124-94-7)
Safety Information
Hazard Codes Xn
Risk Statements 40
Safety Statements 22-36
WGK Germany 3
RTECS TU3850000
HS Code 2937220000
Hazardous Substances Data 124-94-7(Hazardous Substances Data)
Toxicity LD50 subcutaneous in mouse: > 4gm/kg
MSDS Information
Provider Language
SigmaAldrich English
Triamcinolone Usage And Synthesis
Description A natural extension of corticoid research involved examination of compounds containing both a 9α-fluoro group and a double bond between positions 1 and 2. Triamcinolone (9-fluoro-11β, 16α, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna- 1,4-diene-3,20-dione), introduced in 1958, combines the structural features of a ?1 -corticoid and a 9α-fluoro corticoid. As mentioned previously, the 9α-fluoro group increases the anti-inflammatory potency, but it also markedly increases the mineralocorticoid potency. This is undesirable if the drug is to be used internally for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. By inserting a 16α-hydroxy group into the molecule, one can decrease the mineralocorticoid activity.
Chemical Properties White, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; slightly soluble in usual organic solvents; soluble in dimethylformamide.
Originator Kenacort,Squibb,US,1958
Uses A glucocorticoid, antiasthmatic (inhalant); antiallergic (nasal).
Uses Triamcinolone is a glucocorticoid. Triamcinolone is used as an antiasthmatic (inhalant); antiallergic (nasal).
Definition ChEBI: A C21-steroid hormone that is 1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione carrying four hydroxy substituents at positions 11beta, 16alpha, 17alpha and 21 as well as a fluoro substituent at position 9. sed in the form of its 16,17-acetonide to treat various skin infections.
Indications Intralesional bleomycin, a cytotoxic drug that inhibits DNA synthesis, is effective for all varieties of recalcitrant warts. Various concentrations of the drug have been used, although the total dose must be carefully tracked over time to avoid potential systemic toxicity.
Manufacturing Process Preparation of δ1,4-Pregnandiene-9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-Tetrol-16,21- Diacetate: An agar slant of Corynebacterium simplex was washed with 5 ml of sterile saline and the spore suspension added to 100 ml of Trypticase soy broth in a 500 ml Erlenmeyer. The mixture was incubated at 32°C for 8 hr and 1 ml was used to inoculate 10 flasks, each containing 100 ml of Trypticase soy broth. The flasks were incubated with shaking at 32°C for 16 hr. 20 mg δ4- pregnene-9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-tetrol-3,20-dione16,21-diacetate dissolved in 2 ml ethanol was added and the flasks pooled. This solution was extracted several times with methylene chloride, washed with saturated saline and evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in methanol, treated with activated charcoal, filtered through diatomaceous earth and reevaporated to afford 277 mg of oil and acetylated overnight.
Paper strip chromatography showed approximately equal amounts of substrate and a more polar product (δ1,4-pregnadiene-9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-tetrol- 3,20-dione 16,21-diacetate) together with very small amounts of two less polar products. Partition chromatography of 0.25 gram of the residue (diatomaceous earth column; system: 2 parts ethyl acetate, 3 parts petroleum ether (90° to 100°C), 3 parts methanol and 2 parts water) separated the less polar products and the substrate. The desired most polar product remained on the column and was eluted with 500 ml of methanol. The residue (90 mg) from the evaporated methanol was repartitioned on diatomaceous earth [system: 3 parts ethyl acetate, 2 parts petroleum ether (90° to 100°C), 3 parts methanol, and 2 parts water] and the cut containing the desired product (determined by ultraviolet absorption spectrum) was evaporated under reduced pressure to afford 18 mg of solid.
Crystallization from acetone-petroleum ether gave 13 mg of colorless needles of δ1,4-pregnadiene-9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-tetrol-3,20-dione16,21- diacetate; melting point (Kofler block) about 150° to 240°C with apparent loss of solvent at 150°C. Recrystallization from acetone-petroleum ether did not alter the melting point.
Preparation of δ1,4-Pregnadiene-9α-Fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-Tetrol-3,20-Dione: A solution of 100 mg of δ1,4-pregnadiene-9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-tetrol- 3,20-dione16,21-diacetate was dissolved in 10 ml of methanol and cooled to 0°C. After flushing with nitrogen, a solution of 35 mg of potassium hydroxide in 2 ml of methanol was added to the steroid solution. After standing at room temperature for 1 hour, the solution was neutralized with glacial acetic acid and evaporated under a nitrogen atmosphere to a white solid. Water was added, and after cooling, the product was filtered and washed with water to afford 52 mg of δ1,4-pregnadiene-9α-fluoro-11β,16α,17α,21-tetrol-3,20-dione, melting point 246° to 249°C. Three crystallizations from acetone-petroleum ether gave 29 mg of the tetrol, melting point 260° to 262.5°C according to US Patent 2,789,118.
Therapeutic Function Glucocorticoid
Biochem/physiol Actions Triamcinolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid agonist; induces gene expression and apoptosis; inhibits prostaglandin synthesis; impairs tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced degradation of κB-α; potentiates the differentiation-inducing effects of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP-2, -4, -6).
Clinical Use Triamcinolone to be used topically is generally dispensed as its more potent and lipophilic acetonide, a 16α,17α-methylenedioxy cyclic ketal or isopropylidene derivative. It is effective in the treatment of psoriasis and other corticoid-sensitive dermatologic conditions. Topically, triamcinolone acetonide is a more potent derivative of triamcinolone and is approximately eight times more active than prednisolone.
Side effects Even though triamcinolone has an apparently decreased tendency to cause salt and water retention and edema and may induce sodium and water diuresis, it causes other unwanted side effects, including anorexia, weight loss, muscle weakness, leg cramps, nausea, dizziness, and a general toxic feeling.
Safety Profile Poison by subcutaneous route.An experimental teratogen. Other experimentalreproductive effects. Human mutation data reported.When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of F??.An anti-inflammatory and antiallergic agent.
Chemical Synthesis Triamcinolone, 9a-fluoro-11b,16a,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1, 4-dien-3,20-dione (27.1.61), differs from dexamethsone in terms of chemical structure in that the a methyl group at C16 is replaced with a hydroxyl group. It is synthesized from the 21-O-acetate of hydrocortisone 27.1.17. In the first stage, both carbonyl groups of this compound undergo ketalization by ethylene glycol. Next, the hydroxyl group in the resulting diketal 27.1.53 is replaced with chlorine using thionyl chloride, and the product undergoes dehydrochlorination using an alkaline, during which the 21-O-acetyl group also is hydrolyzed. Acetylating the hydroxyl group once again with acetic anhydride gives a triene 27.1.54. Reacting this with osmium tetroxide gives the vicinal diol 27.1.55. The secondary hydroxyl group at C16 of this product undergoes acetylation by acetic anhydride in pyridine, which forms the diacetate 27.1.56. Treating the product with N-bromoacetamide in chloric acid gives a bromohydrin (27.1.57), which upon reaction with potassium acetate is transformed to an epoxide (27.1.58). Opening of the epoxide ring, using hydrofluoric acid, gives the corresponding 9-fluoro-11-hydroxy derivative 27.1.59. Upon microbiological dehydrogenation, the C1–C2 bond is oxidized to a double bond, forming triamcinolone acetate (27.1.60), the acetyl group of which is hydrolyzed, forming the desired triamcinolone (27.1.61).

Drug interactions Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aldesleukin: avoid concomitant use.
Antibacterials: metabolism accelerated by rifamycins; metabolism possibly inhibited by erythromycin; concentration of isoniazid possibly reduced.
Anticoagulants: efficacy of coumarins and phenindione may be altered.
Antiepileptics: metabolism accelerated by carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with amphotericin - avoid; metabolism possibly inhibited by itraconazole and ketoconazole.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: rare reports of convulsions in patients on ciclosporin and high-dose corticosteroids.
Cobicistat: concentration of triamcinolone possibly increased.
Diuretics: enhanced hypokalaemic effects of acetazolamide, loop diuretics and thiazide diuretics.
Vaccines: high dose corticosteroids can impair immune response to vaccines; avoid with live vaccines.
Metabolism Triamcinolone is metabolised largely hepatically but also by the kidney and is excreted in urine. The main metabolic route is 6-beta-hydroxylation; no significant hydrolytic cleavage of the acetonide occurs.
Triamcinolone Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials Triamcinolone diacetate-->soy broth-->Potassium hydroxide-->Pancuronium bromide-->Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 11β,16α,17,21-tetrahydroxy-, 16,21-diacetate-->9-Fluoro-11,16,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 21-acetate-->Budesonide Impurity 18
Preparation Products Triamcinolone acetonide 21-acetate
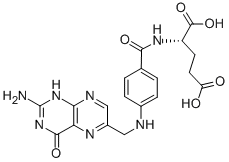 Folic acid,59-30-3
Folic acid,59-30-3
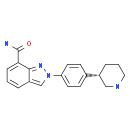 MK-4827 (HCl)
MK-4827 (HCl)
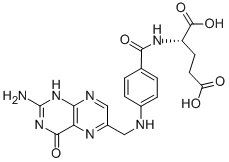 Folic acid
Folic acid
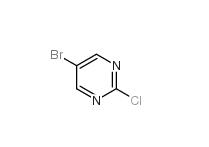 5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5
5-Bromo-2-chloropyrimidine 32779-36-5
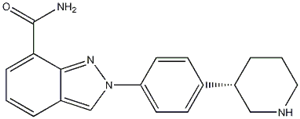 Niraparib
Niraparib
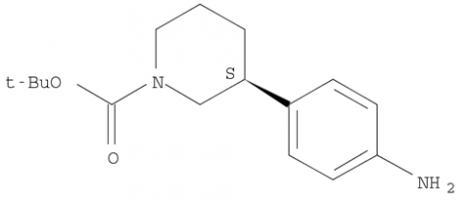 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
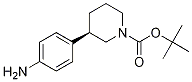 (R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
(R)-tert-butyl 3-(4-aMinophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
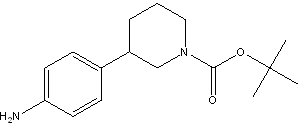 tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-butyl 3-(4-aminophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
![(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester](/data/attachment/201705/26/3446bd2b841689a5afc36447418dc476.png) (3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-[4-[7-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-2H-indazol-2-yl]phenyl]-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
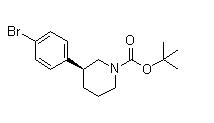 (3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
(3S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-1-piperidinecarboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester
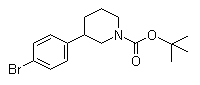 3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
3-(4-Bromophenyl)piperidine-1-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
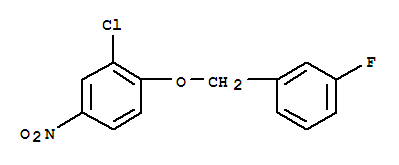 3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
3-Chloro-4-(3-fluorobenzyloxy)nitrobenzene
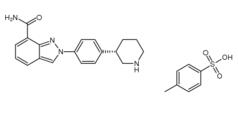 Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate
Niraparib p-toluenesulfonate
![N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/da41ae70b523a458db70333bd1059362.png) N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
N-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-2-[4-(3S)-3-piperidinylphenyl]-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
![2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201705/26/d3114dd994f3dda3142cba7d326bcede.jpg) 2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
2-{4-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]phenyl}-2H-indazole-7-carboxamide
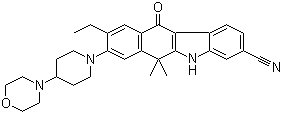 Alectinib
Alectinib
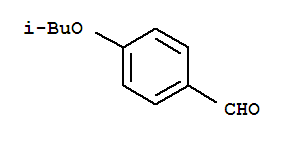 Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)
Benzaldehyde,4-(2-methylpropoxy)
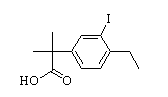 2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid
2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoic acid
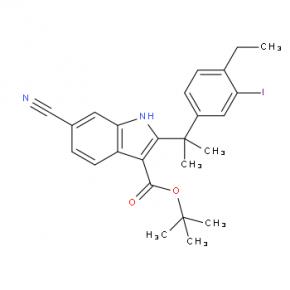 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
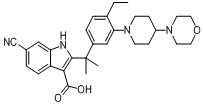 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid
6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid
![9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/e48e5d316800efe6192ebfdeec6cf28c.gif) 9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-ethyl-8-iodo-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
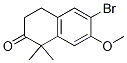 6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one
6-broMo-7-Methoxy-1,1-diMethyl-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one
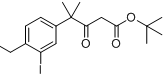 tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate
tert-butyl 4-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-3-oxopentanoate
![9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile](/data/attachment/201705/28/fe98529212eb834b17a38f13138a35bf.png) 9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
9-broMo-8-hydroxy-6,6-diMethyl-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile
![9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride](/data/attachment/201705/28/36e5363f0c9f92378b75195743e2abb2.jpg) 9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
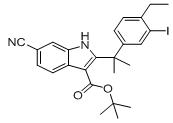 tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
tert-butyl 6-cyano-2-(2-(4-ethyl-3-iodophenyl)propan-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxylate
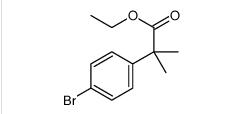 ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate
ethyl 2-(4-broMophenyl)-2-Methylpropanoate
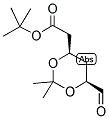 ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate
ert-Butyl (4R-cis)-6-formaldehydel-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4-acetate
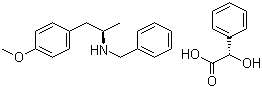 (2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
(2S)-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid (2R)-N-benzyl-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine
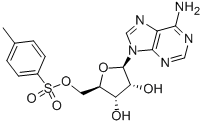 5-Tosyladenosine
5-Tosyladenosine
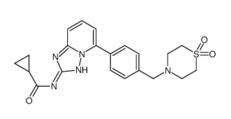 Filgotinib
Filgotinib
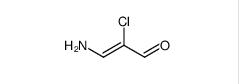 3-amino-2-chloroacrolein
3-amino-2-chloroacrolein
![2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide](/data/attachment/201706/03/2e19d959128718d26901f9909d7b9342.jpg) 2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
2-Methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
![11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine](/data/attachment/201706/03/1549d9affee63ead337049001f25d9fa.jpg) 11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine
11-(1-Methylpiperidin-4-ylidene)-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[d]iMidazo[1,2-a]azepine
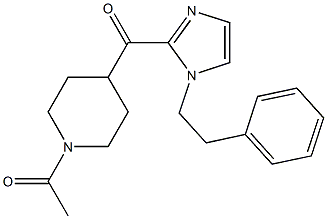 1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE
1-(4-(1-PHENETHYL-1H-IMIDAZOLE-2-CARBONYL)PIPERIDIN-1-YL)ETHANONE
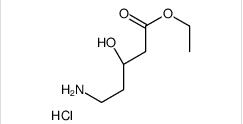 ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride
ethyl (3R)-5-amino-3-hydroxypentanoate,hydrochloride
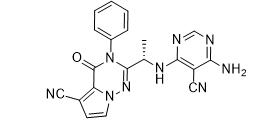 LAS191954 free base
LAS191954 free base
![tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate](/data/attachment/201706/03/8a3c0fcdeb9ed744fc854cf248d4d53e.jpg) tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate
tert-butyl 5-tosyl-5H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazin-2-ylcarbamate
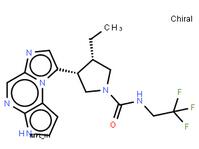 ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2
ABT-494 Intermeidate N-2
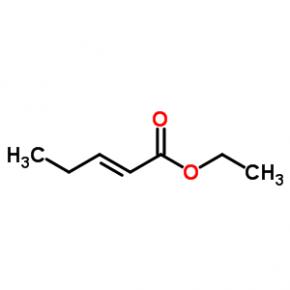 ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate
ethyl (2E)-pent-2-enoate
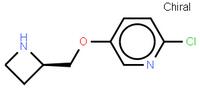 abt594 Intermediate
abt594 Intermediate
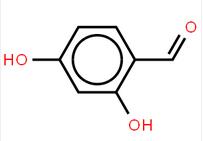 LOXO101 Intermediate 2
LOXO101 Intermediate 2
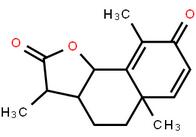 LOXO101 Intermediate 1
LOXO101 Intermediate 1
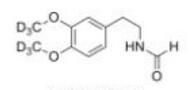 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-2
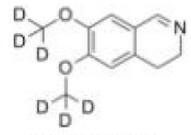 Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1
Deutetrabenazine intermediate N-1
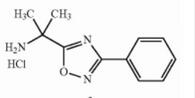 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate
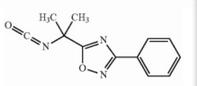 Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2
Naldemedine tosylate intermediate N-2
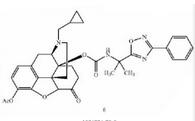 Naldemedine
Naldemedine
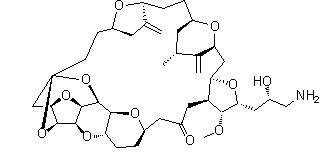 Eribulin
Eribulin
![2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-, 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,](/data/attachment/201706/03/3575f40dcc389832ca73cc99972a645b.gif.thumb.jpg) 2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,
2-Furanpropanol, 5-[2-[(2S,4R,6R)-6-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2S)-2,3-bis[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]propyl]tetrahydro-4-methoxy-3-[(phenylsulfonyl) methyl]-2-furanyl]methyl]tetrahydro-4-methyl-5-methylene-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-methylene-,
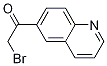 2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone
2-BroMo-1-quinolin-6-yl-ethanone
![6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline](/data/attachment/201706/07/27ae4307b53f4294590fb8f914894490.jpg) 6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline
6-[(6-Bromo-1H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyrazin-1-yl)methyl]-7-fluoroquinoline
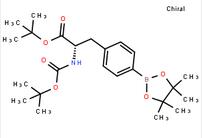 tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate
tert-butyl (S)-2-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-3-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)phenyl)propanoate
![7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine](/data/attachment/201706/07/24ba6100528abe0753ad9e82ef8dc810.gif) 7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine
7-Trifluoromethyl-imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine
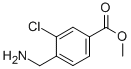 methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate
methyl 4-(aminomethyl)-3-chlorobenzoate
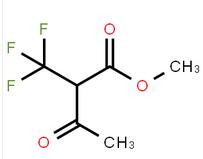 methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate
methyl 3-oxo-2-(trifluoromethyl)butanoate
![2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/07/22aadd4c55094254a681014935f56827.jpg) 2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
2-AMino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-benzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
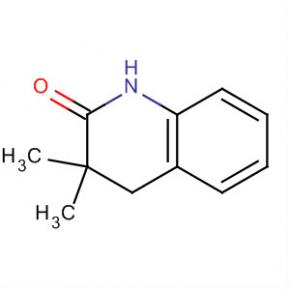 2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl
2(1H)-Quinolinone, 3,4-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl
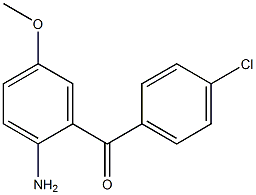 Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)
Methanone, (2-aMino-5-Methoxyphenyl)(4-chlorophenyl)
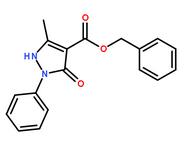 benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
benzyl 5-methyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate
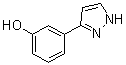 3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol
3-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)phenol
 4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline
4-(1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)aniline
 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2,2-dimethyl-propan-1-ol
 1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol
1-(5-bromo-pyridin-2-yl)-2-methyl-propan-1-ol
![Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)](/data/attachment/201706/07/c4adcbada0ef372ae46cbaed643dd18e.jpg) Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)
Benzenemethanol, a-[(1S)-1-aminoethyl]-4-hydroxy-,(aR)
![2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy](/data/attachment/201706/07/e0e9b5769a45af836d70be4140043125.gif.thumb.jpg) 2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy
2(1H)-Quinolinone,5-[(1R)-2-amino-1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]ethyl]-8-hydroxy
![2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/07/5754ee36bdfbf4148f45632422f563b9.jpg) 2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-{[3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrim idin-2-yl]sulfanyl}-N-(6-methyl-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)acetamide
![2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/47a8b3c98aef0b9ba378c4b7c6cef435.jpg) 2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide
2-((3-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-3,4,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio)-N-(6-methylbenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)acetamide
![N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide](/data/attachment/201706/08/beda6f8f4655aa74d3646cfc7621fb20.jpg) N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide
N-(6-Methyl-2-benzothiazolyl)-2-[(3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-4-oxo-3-phenylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)thio]-acetamide
 (R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane
(R)-(-)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-benzylaminopropane
![4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl] 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]](/data/attachment/201706/09/b600ffca12695094db2c5f6045cb6685.jpg) 4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]
4(3H)-Quinazolinone,7-bromo-6-chloro-3-[3-(3-hydroxy-2-piperidinyl)-2-oxopropyl]
![9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID](/data/attachment/201706/09/d6b395bbfb23e628be7d536d9cc2b512.gif) 9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
9-OXO-1,2,3,9-TETRAHYDRO-PYRROLO[2,1-B]QUINAZOLINE-6-CARBOXYLIC ACID
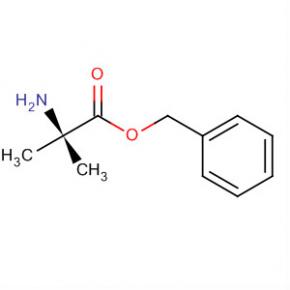 Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester
Alanine, 2-methyl-, phenylmethyl ester
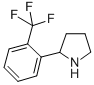 2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE
2-(2-TRIFLUOROMETHYL-PHENYL)-PYRROLIDINE
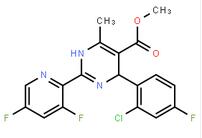 (-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
(-)-4(R)-(2-Chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-2-(3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
![2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester](/data/attachment/201706/09/11c6e17ba89840528c5461ae5350df33.gif) 2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
2-Butenoic acid, 2-hydroxy-4-[5-(1-Methylethyl)-2,4-bis(phenylMethoxy)phenyl]-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
methanone [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone](/data/attachment/201706/09/ca947be16560699c92609cd96b352c02.png.thumb.jpg) [4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone
[4-amino-2-(ethylsulfanyl)pyrimidin-5-yl](2,3-difluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)methanone
![Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl](/data/attachment/201706/10/ce0d621896c03bdb67e3b184103e84ff.png.thumb.jpg) Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl
Benzenesulfonamide, 2-[(5-bromo-2-chloro-4-pyrimidinyl)amino]-N-methyl
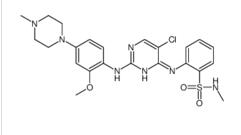 ALK inhibitor 2
ALK inhibitor 2
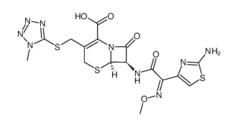 Cefmenoxime hydrochloride
Cefmenoxime hydrochloride
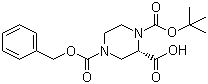 (S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid
(S)-N-1-Boc-N-4-Cbz-2-piperazinecarboxylic acid
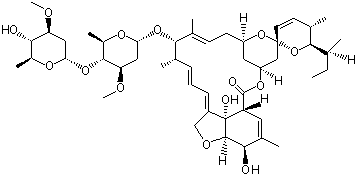 Avermectin
Avermectin
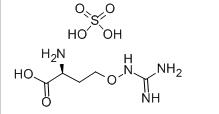 L-CANAVANINE SULFATE
L-CANAVANINE SULFATE
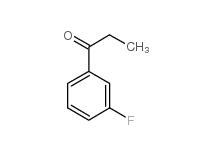 3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4
3-Fluoropropiophenone 455-67-4
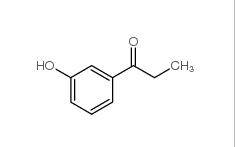 3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5
3-Hydroxypropiophenone 13103-80-5
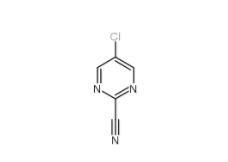 2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8
2-Cyano-5-chloropyrimidine 38275-56-8
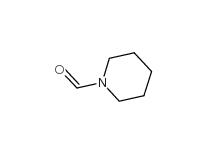 N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8
N-Formylpiperidine 2591-86-8
 Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3
Indazole-3-carboxylic acid 4498-67-3
 5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9
5-Bromo-2-cyanopyrimidine 38275-57-9
 4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2
4,4-Dibromobenzophenone 3988-03-2
![1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8](/data/attachment/201901/28/b183df1e648eca4396ad0d319a1254bc.jpg) 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-benzo[b]azepin-5-one 1127-74-8
 4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6
4038-14-6,(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone 4038-14-6
 2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1
2-Amino-5-bromopyrimidine 7752-82-1
 Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8
Triphenylbismuth 603-33-8
![3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4](/data/attachment/201901/28/d6294d1dabcee85ee04792b0c0e255c0.jpg) 3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4
3-Ethynylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine 943320-53-4
 4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5
4-Nitrophenylacetonitrile 555-21-5
 2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0
2-(4-aminophenyl)acetonitrile 3544-25-0
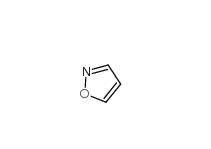 isoxazole 288-14-2
isoxazole 288-14-2
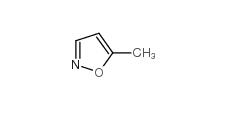 5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6
5-Methylisoxazole 5765-44-6
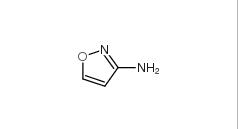 3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1
3-Aminoisoxazole 1750-42-1
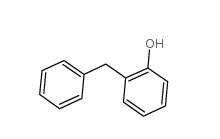 2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4
2-Hydroxydiphenylmethane 28994-41-4
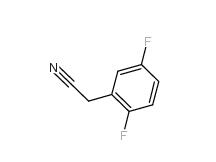 2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8
2,5-Difluorobenzyl Cyanide 69584-87-8
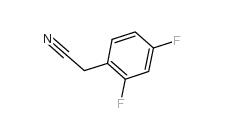 2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9
2,4-Difluorophenylacetonitrile 656-35-9
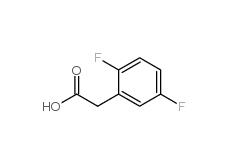 2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5
2,5-Difluorophenylacetic acid 85068-27-5
 2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3
2,4-Difluorophenylacetic acid 81228-09-3
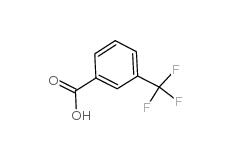 3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2
3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid 454-92-2
![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3](/data/attachment/201901/29/22b99245cb0bbcd2d86f238725d9fb9d.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetonitrile 2338-76-3
![2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9](/data/attachment/201901/29/7dbc74a276a4c124b9460222442fd80f.jpg) 2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9
2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetic acid 351-35-9
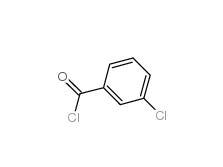 3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2
3-Chlorobenzoyl chloride 618-46-2
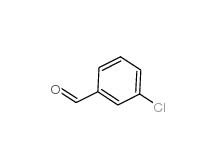 3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2
3-Chlorobenzaldehyde 587-04-2
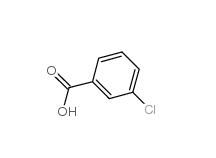 3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8
3-chlorobenzoic acid 535-80-8
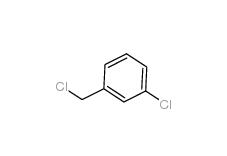 3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2
3-Chlorobenzyl chloride 620-20-2
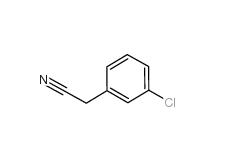 3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5
3-Chlorobenzyl cyanide 1529-41-5
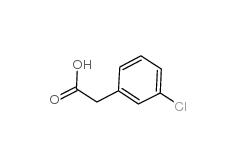 2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5
2-(3-chlorophenyl)acetic acid 1878-65-5
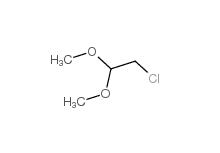 Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2
Dimethylchloroacetal 97-97-2
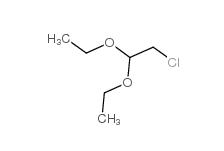 Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5
Chloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal 621-62-5
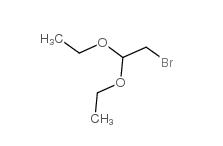 2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1
2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane 2032-35-1
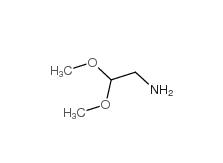 2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6
2,2-dimethoxyethanamine 22483-09-6
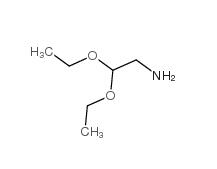 2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3
2,2-Diethoxyethylamine 645-36-3
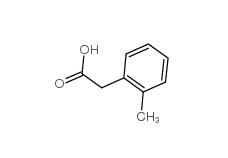 2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0
2-Methylphenylacetic acid 644-36-0
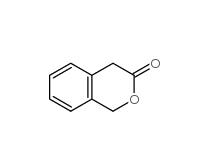 3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7
3-Isochromanone 4385-35-7
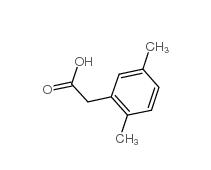 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetic acid 13612-34-5
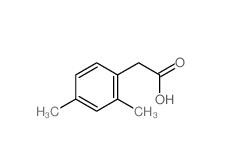 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid 6331-04-0
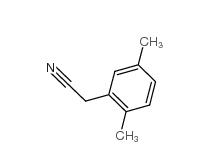 2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7
2,5-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 16213-85-7
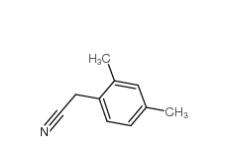 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetonitrile 68429-53-8
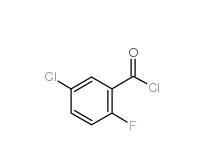 5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6
5-CHLORO-2-FLUOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 394-29-6
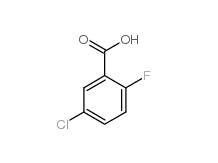 5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9
5-Chloro-2-fluorobenzoic acid 394-30-9
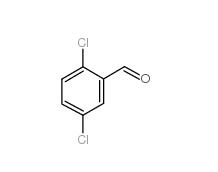 2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5
2,5-Dichlorobenzaldehyde 6361-23-5
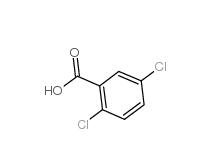 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 50-79-3
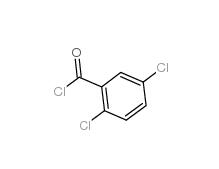 2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5
2,5-DICHLOROBENZOYL CHLORIDE 2905-61-5
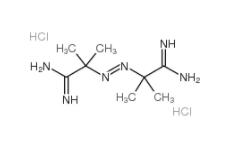 2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4
2,2-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride 2997-92-4
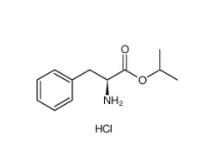 L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7
L-Phenylalanine, 1-methylethyl ester, hydrochloride 95585-78-7
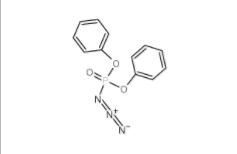 Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9
Diphenylphosphoryl azide 26386-88-9
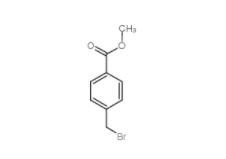 Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3
Methyl 4-(bromomethyl)benzoate 2417-72-3
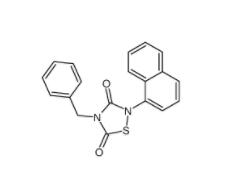 Tideglusib 865854-05-3
Tideglusib 865854-05-3
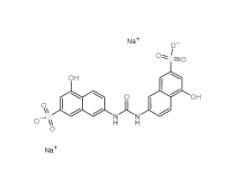 Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2
Disodium 7,7-(carbonyldiimino)bis(4-hydroxynaphthalene-2-sulphonate) 20324-87-2
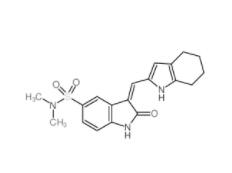 SU 6656 330161-87-0
SU 6656 330161-87-0
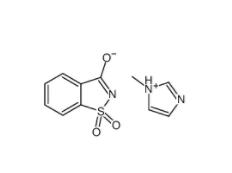 Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4
Saccharin 1-methylimidazole 482333-74-4
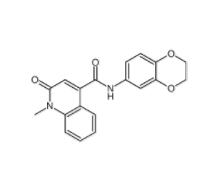 CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8
CeMMEC13 1790895-25-8
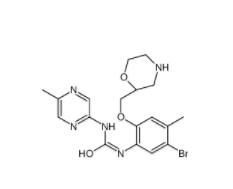 Rabusertib 911222-45-2
Rabusertib 911222-45-2
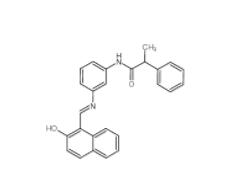 Salermide 1105698-15-4
Salermide 1105698-15-4
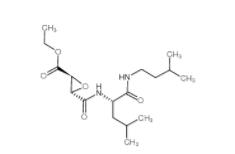 EST 88321-09-9
EST 88321-09-9
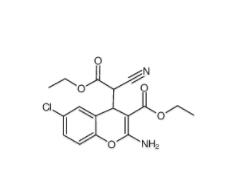 SC79 305834-79-1
SC79 305834-79-1
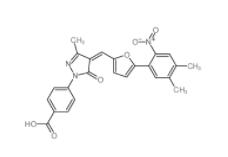 C646 328968-36-1
C646 328968-36-1
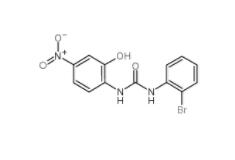 1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4
1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxy-4-nitrophenyl)urea 182498-32-4
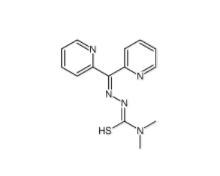 Dp44mT 152095-12-0
Dp44mT 152095-12-0
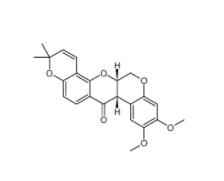 Deguelin 522-17-8
Deguelin 522-17-8
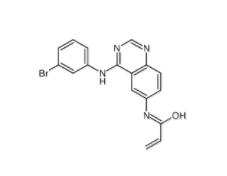 PD168393 194423-15-9
PD168393 194423-15-9
 YO01027 209984-56-5
YO01027 209984-56-5
 DC10539 1822358-25-7
DC10539 1822358-25-7
 8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4
8-OH-DPAT 78950-78-4
 YU238259 1943733-16-1
YU238259 1943733-16-1
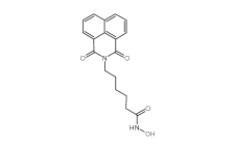 Scriptaid 287383-59-9
Scriptaid 287383-59-9
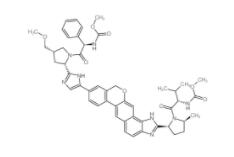 Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7
Velpatasvir 1377049-84-7
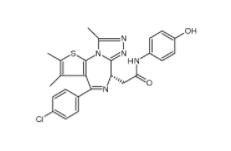 OTX015 202590-98-5
OTX015 202590-98-5
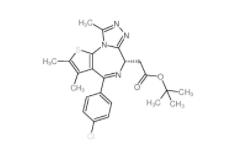 (+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4
(+)-JQ-1 1268524-70-4
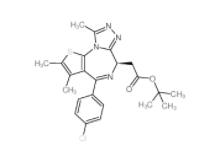 (-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5
(-)-JQ-1 1268524-71-5
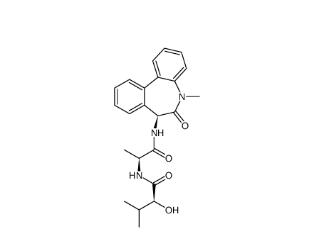 LY 900009 209984-68-9
LY 900009 209984-68-9
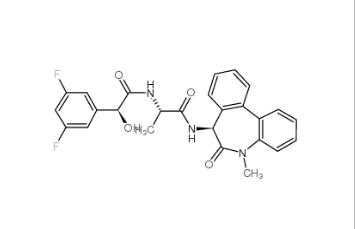 LY-411575 209984-57-6
LY-411575 209984-57-6
![(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3 (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3](/data/attachment/201903/22/9e81dae7e0bdec56ac6052b1872d9626.jpg) (4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3
(4-nitrophenyl) 4-[bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-hydroxymethyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate 1101854-58-3
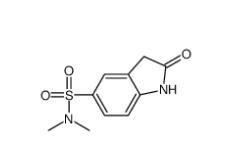 N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6
N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,3-dihydroindole-5-sulfonamide 170565-89-6
![5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/50930df6d55412ac8f4da0724b497aaf.jpg) 5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9
5,6,11,12-tetrahydrodibenzo[1,2-b:1,2-g][8]annulene 1460-59-9
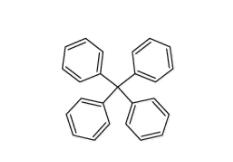 Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2
Tetraphenylmethane 630-76-2
![2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2](/data/attachment/201903/23/7e63bafe6c4b7e146e00c57dfca99672.jpg) 2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2
2-chloro-6-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-1-naphthalen-2-ylpropan-2-yl)amino]propoxy]benzonitrile 284035-33-2
 1616380-54-1
1616380-54-1
![N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9 N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9](/data/attachment/201903/23/e26baac537719657acd9f1f55568401d.jpg) N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9
N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxin-6-yl)-2-methyl-1-oxo-1,2-dihydroisoquinoline-4-carboxamide 440662-09-9
![N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0 N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0](/data/attachment/201903/23/7d2bbd100c8322ae16168937617e1bb2.jpg) N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0
N-[2-[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]ethyl]butanamide 932986-18-0
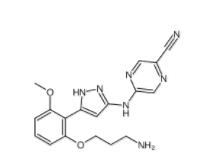 5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1
5-(5-(2-(3-aminopropoxy)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-ylamino)pyrazine-2-carbonitrile 1234015-52-1
![3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6](/data/attachment/201903/23/07bf6fd99e81033df0c83039ccdde036.jpg) 3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6
3-Methyl-3-[(1E)-2-phenylethenyl]-3,2:5,2:5,3-quaterpyridine 1651890-44-6
![3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3](/data/attachment/201903/23/f69ad7342d131146640e0c88f73e9a25.jpg) 3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3
3-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-biphenylyl]-1,1-dimethylure 1469924-27-3
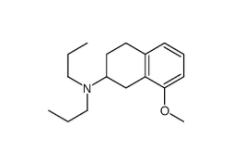 8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7
8-Methoxy-N,N-dipropyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-2-naphthalenamine 3897-94-7
![4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7](/data/attachment/201903/23/bb4110673d0676f81860d708092eb660.jpg) 4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7
4-{4-[(4-{[3-(Acryloylamino)phenyl]amino}-5-fluoro-2-pyrimidinyl) amino]phenoxy}-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide 1202759-32-7
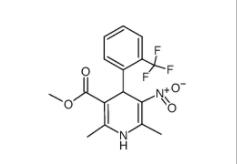 1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4
1,4-Dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-3-nitro-4-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)-pyridine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 71145-03-4
![2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4](/data/attachment/201903/23/b396a2326dddb511aae497b01fbd4c77.jpg) 2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4
2-[[3-[[2-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methyl]-2-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-diazinan-1-yl]methyl]-N,N-dimethylaniline 500579-04-4
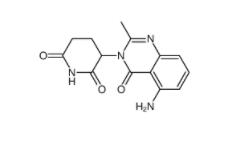 CC-122 1015474-32-4
CC-122 1015474-32-4
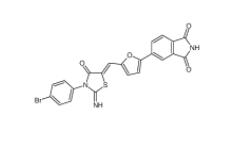 Bioymifi 1420071-30-2
Bioymifi 1420071-30-2
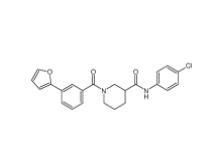 N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(3-(furan-2-yl)benzoyl)piperidine-3-carboxamide 1443437-74-8
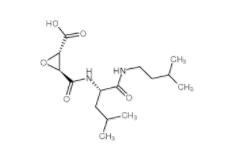 E-64C 76684-89-4
E-64C 76684-89-4
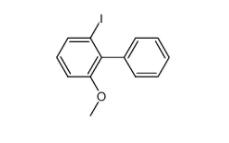 2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1
2-iodo-6-methoxybiphenyl 84253-78-1
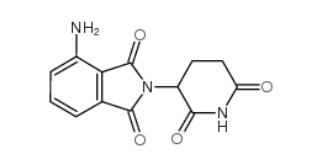 pomalidomide 19171-19-8
pomalidomide 19171-19-8
 4EP-Directory listing
4EP-Directory listing
 Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9
Stearoylbenzoylmethane 58446-52-9
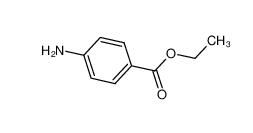 benzocaine 94-09-7
benzocaine 94-09-7
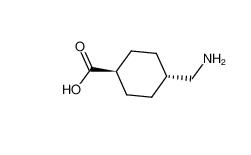 tranexamic acid 1197-18-8
tranexamic acid 1197-18-8
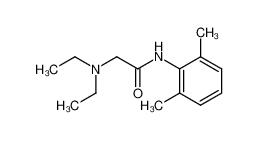 lidocaine 137-58-6
lidocaine 137-58-6
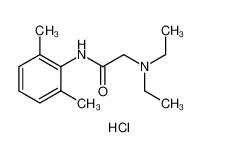 lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9
lidocaine hydrochloride 73-78-9
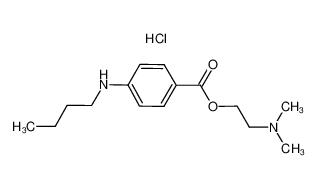 Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0
Tetracaine hydrochloride 136-47-0
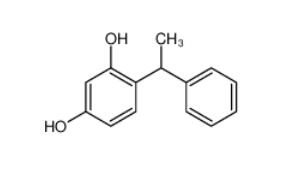 4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8
4-(1-phenylethyl)benzene-1,3-diol 85-27-8
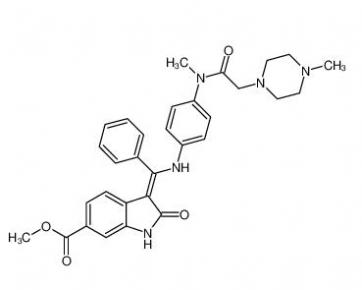 Nintedanib 656247-17-5
Nintedanib 656247-17-5
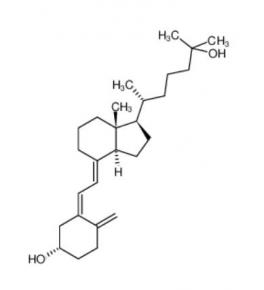 calcidiol 19356-17-3
calcidiol 19356-17-3
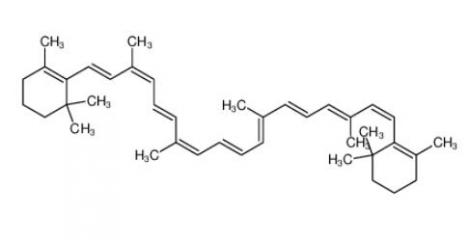 β-carotene 7235-40-7
β-carotene 7235-40-7
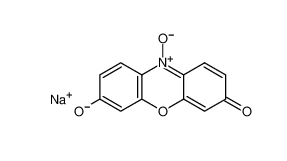 Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8
Resazurin sodium salt 62758-13-8
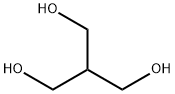 4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL
4704-94-3 2-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIOL
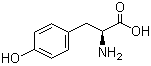 L-Tyrosine 60-18-4
L-Tyrosine 60-18-4
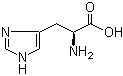 L-Histidine 71-00-1
L-Histidine 71-00-1
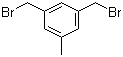 3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3
3,5-Bis(bromomethyl)toluene 19294-04-3
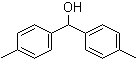 Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8
Bis(4-methylphenyl)methanol 885-77-8
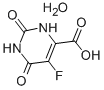 5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4
5-Fluoroorotic Acid Hydrate 207291-81-4
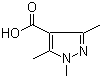 1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7
1,3,5-Trimethyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid 1125-29-7
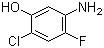 5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8
5-Amino-2-chloro-4-fluorophenol 84478-72-8
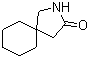 Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9
Gabapentin-lactam 64744-50-9
 1EP-Directory listing
1EP-Directory listing
![[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3 [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3](/data/attachment/202211/10/9756043560e11c17cf958f3ed54d541a.png.thumb.jpg) [2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3
[2-(aminocarbonyl)phenyl]acetic acid 23362-56-3
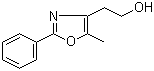 2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4
2-(5-Methyl-2-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-yl)ethan-1-ol 103788-65-4
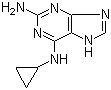 2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7
2-Amino-6-cyclopropylamino-9H-purine 120503-69-7
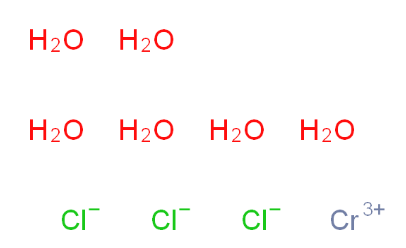 Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5
Chromic chloride hexahydrate 10060-12-5
 2EP-Directory listing 2
2EP-Directory listing 2
 3EP-Directory listing 3
3EP-Directory listing 3
